Wind Energy: Harnessing the Wind for a Sustainable Future
In the quest for cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, wind energy has emerged as a key player in the global shift away from fossil fuels. With its ability to generate vast amounts of power without emitting harmful greenhouse gases, wind energy is becoming an essential part of the renewable energy mix. But what is wind energy, how does it work, and what makes it such an important part of our clean energy future? This article will explore everything you need to know about wind energy, from its origins to its impact on the environment and economy.

What is Wind Energy?
Wind energy is a form of renewable energy that is generated by converting the kinetic energy of wind into usable electricity. This is done through the use of wind turbines, which capture the energy in the moving air and turn it into mechanical energy. The mechanical energy is then converted into electrical energy, which can be used to power homes, businesses, and industries.
Wind energy is one of the cleanest and most sustainable forms of energy. It does not produce air pollution, water pollution, or greenhouse gas emissions, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels.
How Wind Energy Works
Wind energy is harnessed using wind turbines, large structures that are designed to capture the kinetic energy of the wind. Here’s a breakdown of how the process works:
1. Wind Turbines: The Key Technology
A wind turbine consists of several key components that work together to capture the wind’s energy:
- Blades: These large, aerodynamically designed blades are responsible for capturing the wind’s energy. When the wind blows, it causes the blades to spin.
- Rotor: The rotor is made up of the blades and the hub that holds them. As the blades spin, they rotate the rotor.
- Nacelle: The nacelle is the housing that contains the components necessary for generating electricity, such as the gearbox and generator.
- Gearbox: The gearbox amplifies the rotation of the rotor, making it fast enough to generate electricity.
- Generator: The generator converts the mechanical energy from the rotating blades into electrical energy.
2. The Process of Generating Electricity
- Wind blows: As wind moves across the surface of the earth, it creates moving air that has kinetic energy.
- Blades spin: The kinetic energy of the wind causes the blades of the wind turbine to spin, which turns the rotor.
- Mechanical to electrical: The spinning rotor turns the generator, which converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Transmission: The electricity is sent through wires to a transformer, where it is converted into the appropriate voltage and sent to the grid to power homes and businesses.
3. Offshore vs. Onshore Wind Energy
Wind energy can be harnessed both onshore (on land) and offshore (in bodies of water). Offshore wind turbines are typically much larger than their onshore counterparts and are capable of generating more energy due to the stronger, more consistent winds over the ocean.
- Onshore wind energy: This is the most common type of wind energy, where wind turbines are placed on land, usually in rural areas with open, unobstructed winds.
- Offshore wind energy: Offshore wind farms are located in oceans or large lakes, where the wind speeds are generally higher and more consistent.
The Benefits of Wind Energy
Wind energy offers numerous advantages, making it an appealing option for sustainable power generation:
1. Renewable and Abundant
Wind is a renewable resource, meaning it will never run out as long as the earth experiences wind. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite, wind energy is constantly replenished by natural forces like the sun and weather patterns.
2. Clean and Environmentally Friendly
One of the most significant benefits of wind energy is that it is a clean source of energy. Wind turbines generate electricity without emitting harmful pollutants like carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), or nitrogen oxides (NOx). This helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, combat climate change, and improve air quality.
3. Cost-Effective
Wind energy is one of the most cost-effective forms of renewable energy. Once a wind turbine is installed, the cost of producing electricity is minimal, especially when compared to the rising costs of fossil fuels. The cost of wind energy has dropped dramatically over the past decade, making it an increasingly affordable option for countries and businesses around the world.
4. Job Creation and Economic Growth
The wind energy sector has created thousands of jobs worldwide in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. As more countries and companies invest in wind energy, the industry will continue to drive economic growth and provide employment opportunities.
5. Energy Independence
Wind energy can help countries achieve greater energy independence by reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. By harnessing domestic wind resources, nations can strengthen their energy security and stabilize energy prices.
Challenges of Wind Energy
While wind energy offers many benefits, there are still challenges that need to be addressed:
1. Intermittency and Variability
Wind energy is intermittent, meaning that it depends on the availability of wind. This can make it challenging to rely on wind power alone to meet energy demand. To mitigate this issue, wind energy is often used in combination with other renewable sources, such as solar power, or with energy storage systems to ensure a consistent supply.
2. Impact on Wildlife
Wind turbines can have an impact on local wildlife, particularly birds and bats, which may collide with the blades. However, ongoing research and innovations in turbine design are helping to reduce these risks.
3. Space Requirements
Wind farms require large areas of land or water to be effective. This can be a challenge in densely populated areas or regions where space is limited. However, offshore wind farms have addressed this issue by using bodies of water for energy generation.
The Future of Wind Energy
The future of wind energy is incredibly promising, with continuous advancements in technology and increasing investment in renewable energy. Some key trends and developments include:
1. Larger and More Efficient Turbines
Wind turbines are getting larger and more efficient, allowing for greater energy generation at lower costs. Innovations in turbine design, such as vertical-axis turbines, are also being explored to improve efficiency and reduce the impact on wildlife.
2. Floating Wind Farms
One exciting development in offshore wind energy is the rise of floating wind farms. These turbines are located in deep waters where traditional fixed-bottom turbines cannot be installed. Floating wind farms have the potential to unlock vast new areas for wind energy production.
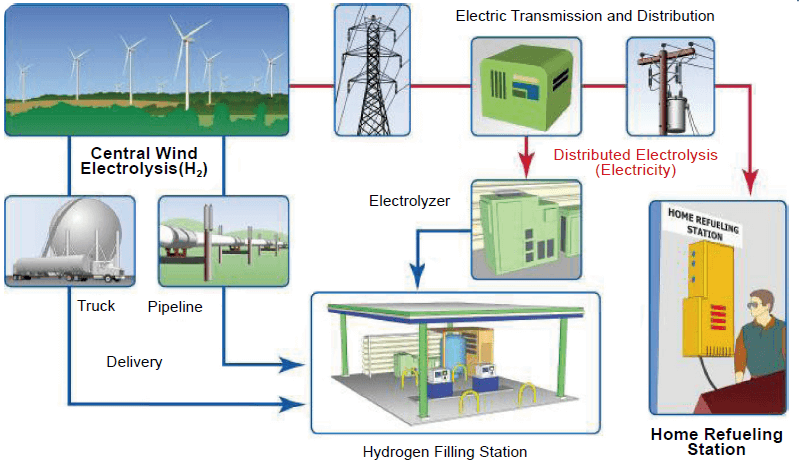
3. Wind-Hydrogen Integration
Wind energy can be used to produce hydrogen through a process called electrolysis, where electricity is used to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. This hydrogen can then be used as a clean fuel for industries like transportation and manufacturing.
FAQs About Wind Energy
1. How much energy does wind energy produce?
The amount of energy produced by a wind turbine depends on its size, location, and the wind speeds in the area. On average, a single wind turbine can produce between 1.5 to 3 megawatts (MW) of electricity.
2. What are the environmental impacts of wind energy?
While wind energy is a clean source of power, it can have some environmental impacts, such as the potential for bird and bat collisions and the land or ocean space required for wind farms. However, these impacts are minimal compared to fossil fuels.
3. Is wind energy cost-effective?
Yes, wind energy is one of the most cost-effective renewable energy sources available. The cost of wind energy has fallen dramatically over the past decade, making it competitive with traditional fossil fuels in many regions.
4. Where are the best places to install wind turbines?
The best places for wind energy installations are areas with consistent, strong winds. This includes rural areas, offshore locations, and certain mountain ranges. Many countries with vast coastlines or plains are ideal candidates for wind farms.
Conclusion
Wind energy is a powerful and sustainable solution to the world’s growing energy needs. By harnessing the wind, we can generate clean electricity, reduce our dependence on fossil fuels, and mitigate climate change. As technology continues to improve and costs continue to fall, wind energy will play an increasingly important role in the global transition to renewable energy.

By investing in wind energy today, we can create a cleaner, more sustainable future for generations to come.

