The Environmental Impact of Smartphones: Understanding the Cost of Convenience
Smartphones have become indispensable to modern life, with over 6.8 billion users globally. They serve as communication tools, work assistants, entertainment hubs, and even financial managers. However, with this growing reliance on smartphones comes an environmental cost that many users may not fully realize. The environmental impact of smartphones is a significant concern, as their production, usage, and disposal contribute to several environmental issues, including electronic waste, energy consumption, and the depletion of natural resources.
In this article, we will explore the various environmental consequences of smartphones, their lifecycle, and how you can help reduce their negative impact. We’ll also look at how the industry is addressing these issues and what steps you can take as a consumer to make more sustainable choices.

The Lifecycle of a Smartphone: A Close Look at Its Environmental Cost
Smartphones have a relatively short lifespan. On average, people replace their phones every 2-3 years, contributing to an increasing volume of electronic waste (e-waste). But the environmental impact starts long before you decide to dispose of your device.
1. Production and Resource Extraction
The production of a smartphone requires various natural resources, including precious metals such as gold, silver, copper, and rare earth elements like lithium and cobalt. Mining these materials has a significant environmental impact, leading to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and the release of toxic chemicals into the environment. Additionally, the extraction process often occurs in countries with limited environmental regulations, exacerbating the problem.
Environmental Concerns of Resource Extraction:
- Deforestation: Large-scale mining operations can lead to the destruction of forests and wildlife habitats.
- Water Pollution: The chemicals used in mining can contaminate water sources, harming both ecosystems and human populations.
- Carbon Emissions: The transportation and processing of these materials require substantial energy, contributing to global carbon emissions.
2. Manufacturing
The manufacturing process of smartphones involves assembling numerous components, each with its own environmental footprint. From the assembly lines to the factories, this process requires substantial energy consumption and emits greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming. In addition, many components, like the battery and display, are difficult to recycle or dispose of safely, exacerbating the environmental challenges.
Some of the key environmental impacts of manufacturing include:
– Energy Consumption: Factories use vast amounts of energy to assemble smartphones and produce their individual components.
– Waste Generation: Production generates a significant amount of waste materials, many of which are non-recyclable.
– Chemical Pollution: The use of hazardous chemicals in the manufacturing process can lead to air and water pollution.
3. Usage
Once a smartphone is in the hands of a user, its environmental impact doesn’t stop there. The energy consumption of smartphones, while relatively low compared to other electronic devices, still contributes to overall global electricity demand. In countries with heavy reliance on fossil fuels for electricity generation, this can result in increased carbon emissions.
Furthermore, as smartphones evolve, many features such as high-resolution screens and power-hungry processors require more energy to run efficiently. This means that the environmental impact of using a smartphone continues throughout its life cycle.
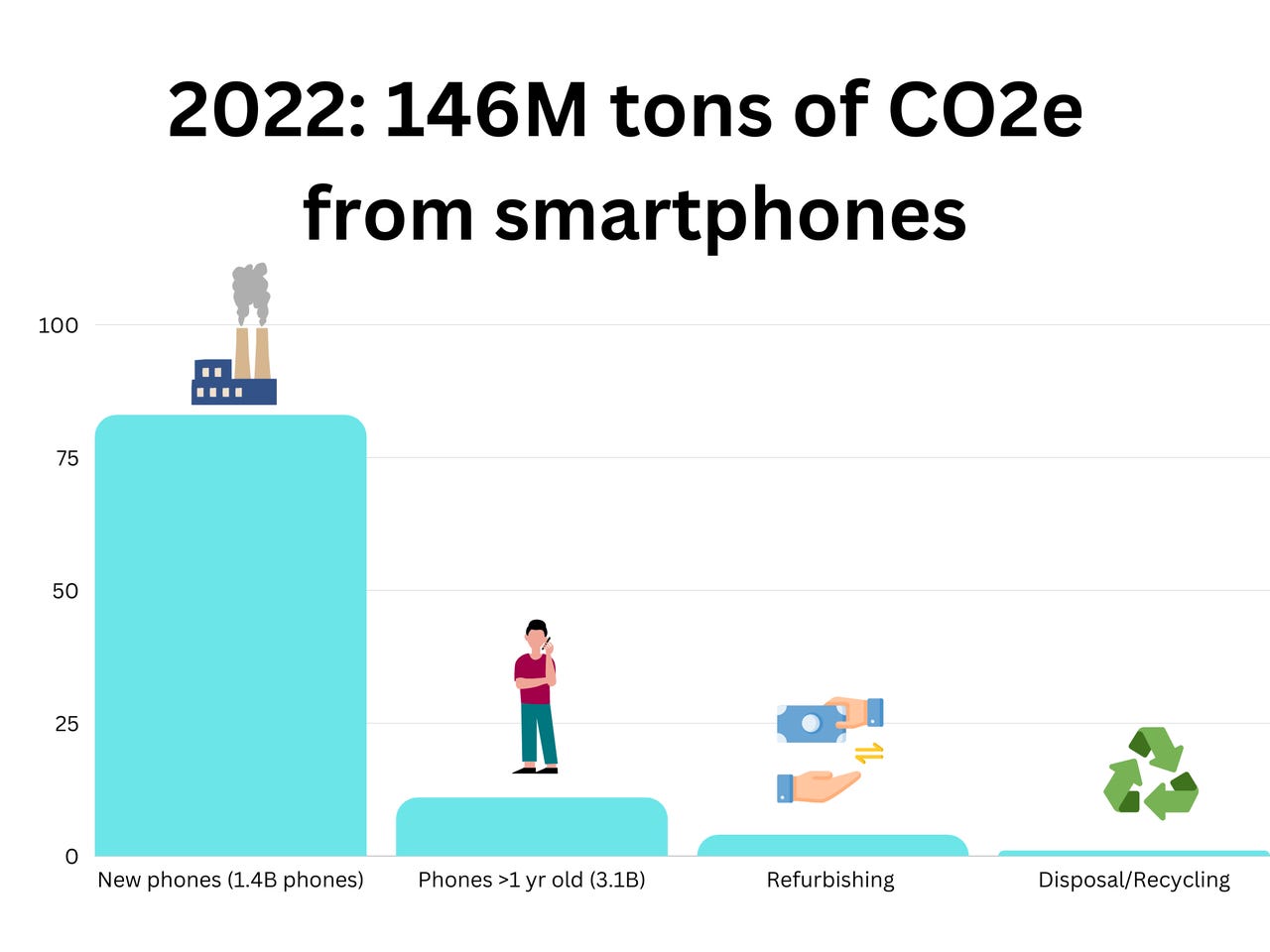
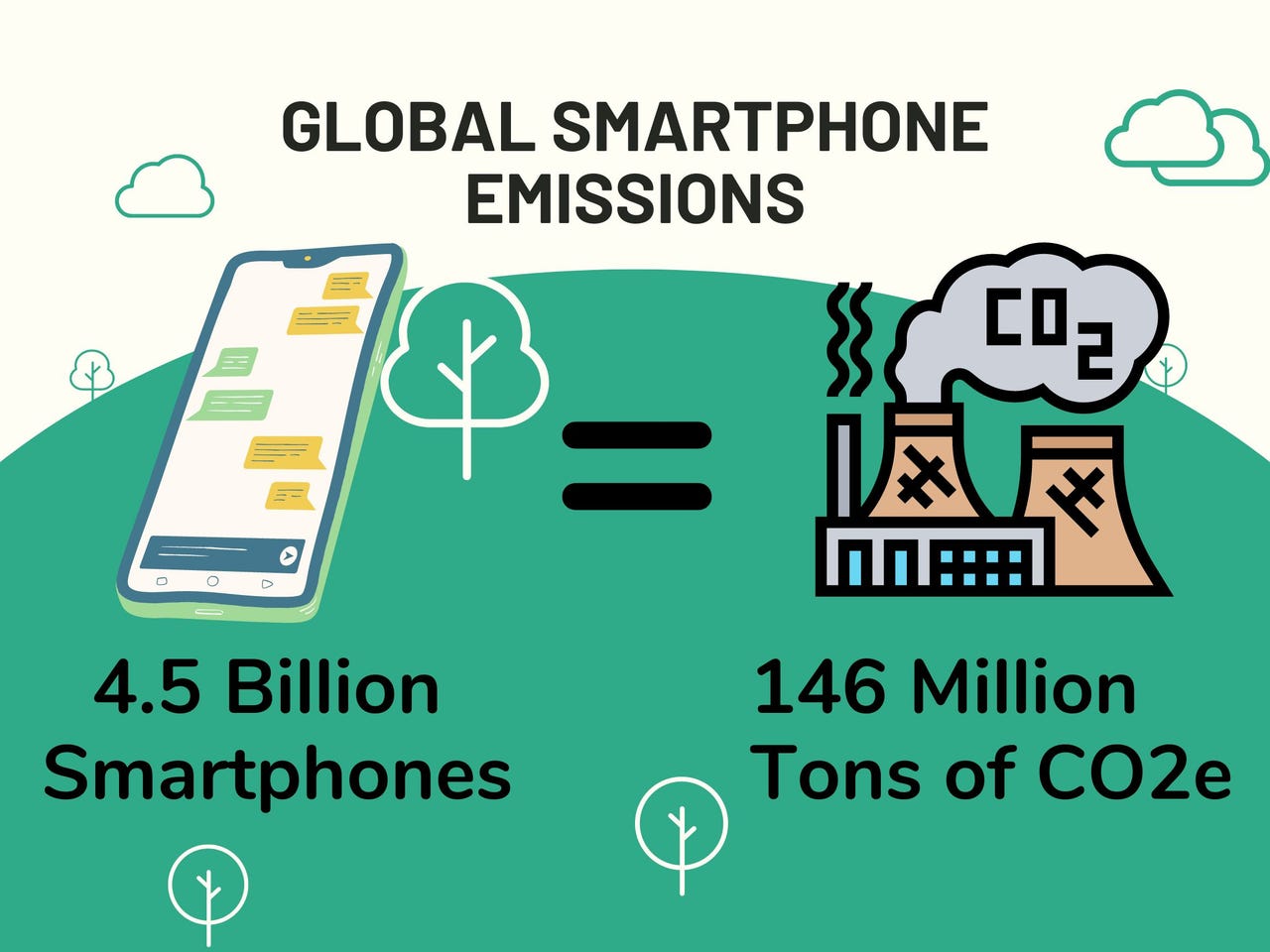
The Issue of E-Waste: A Growing Crisis
As smartphones reach the end of their lifecycle, they often end up in landfills or are incinerated, contributing to the growing issue of electronic waste (e-waste). The recycling rate of smartphones is alarmingly low, and this e-waste can lead to toxic substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium leaching into the soil and water supply, posing risks to both environmental and human health.
- Global E-Waste Statistics: According to a report by the United Nations, nearly 53.6 million metric tons of e-waste were generated globally in 2019, with smartphones being a large contributor.
- Recycling Challenges: Smartphones are difficult to recycle due to their compact nature and the presence of mixed materials like metals, plastics, and glass.
The environmental impact of e-waste is profound, with many phones never reaching a recycling facility. Instead, they end up being incinerated or discarded improperly, contributing to pollution and posing health risks for communities living near landfills.
What Can Be Done: Sustainable Alternatives and Solutions
While the environmental impact of smartphones may seem overwhelming, there are several ways to mitigate the damage. The industry is making strides toward sustainability, and consumers can also make informed choices to reduce their ecological footprint.
1. Sustainable Manufacturing and Design
Several smartphone manufacturers are incorporating sustainable practices into their production processes. For instance, Fairphone, a Dutch smartphone company, designs phones with replaceable parts, encouraging users to repair rather than replace their devices. Moreover, some brands are focusing on recyclable materials, carbon neutrality, and greener manufacturing practices.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Some companies are using recycled plastics, biodegradable components, and responsibly sourced metals.
- Modular Phones: Companies like Fairphone and Google have introduced modular designs where users can replace individual components, like the screen or battery, rather than replacing the entire phone.

2. Extending the Lifespan of Your Smartphone
One of the best ways to reduce the environmental impact of smartphones is to extend their lifespan. By holding on to your device for a longer period and repairing it instead of upgrading frequently, you can significantly reduce your contribution to e-waste.
- Battery Replacement: Instead of buying a new phone when your battery starts to degrade, consider replacing the battery.
- Software Updates: Many manufacturers provide software updates to keep older models running smoothly. Make sure to install updates regularly to ensure your phone performs optimally.
- Phone Repairs: Opt for repairs instead of upgrading your phone every few years. Many issues, from cracked screens to malfunctioning cameras, can be fixed without buying a new device.
3. Recycling and Responsible Disposal
If you decide to upgrade your phone or it’s no longer functional, make sure to recycle it responsibly. Electronic recycling programs allow for the safe disposal of smartphones, ensuring that valuable materials can be extracted and reused.
- Recycling Programs: Many smartphone manufacturers, including Apple and Samsung, offer trade-in and recycling programs that allow users to return their old devices for proper disposal or refurbishment.
- E-Waste Collection Events: Many communities host e-waste recycling events, where you can drop off old electronics for safe disposal.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long do smartphones typically last?
Smartphones typically last between 2 to 3 years before performance issues like slow speeds and battery degradation encourage users to upgrade. However, regular maintenance, repairs, and software updates can help extend a phone’s lifespan.
2. What is the environmental impact of using a smartphone?
While smartphones themselves consume relatively little energy during use, the environmental impact comes from their production, resource extraction, and eventual disposal. The materials used in smartphones, such as lithium, cobalt, and rare earth metals, are sourced through environmentally harmful mining practices.
3. How can I recycle my old smartphone?
You can recycle your old smartphone by participating in manufacturer trade-in programs, using e-waste collection services, or taking it to a local electronics recycling center. Many retailers and phone carriers offer recycling services, making it easier for you to dispose of your device responsibly.
Conclusion
The environmental impact of smartphones is a complex issue that involves resource extraction, manufacturing, energy consumption, and e-waste. However, by making sustainable choices in both manufacturing and consumer behavior, we can reduce the negative effects of smartphones on the planet. By opting for eco-friendly phones, extending the lifespan of our devices, and participating in recycling programs, we can minimize our contribution to the growing problem of e-waste.
It’s clear that smartphones are not going away, but as consumers, we have the power to make a difference. Start by making informed decisions about your next smartphone purchase, maintaining your current device, and recycling it responsibly when the time comes.
By embracing sustainability in smartphone
usage, we can ensure that the future of communication and technology remains bright — without costing the earth.

