The Environmental Impact of Digital Use: Unveiling the Hidden Costs
In our increasingly digital world, we often forget that our constant use of devices, social media, and online services doesn’t just have personal or societal consequences—it also has a significant environmental impact. From energy consumption to electronic waste, the digital ecosystem leaves a heavy carbon footprint. In this article, we will explore the hidden environmental costs of our digital habits, discuss how they affect the planet, and explore ways we can reduce our environmental impact.
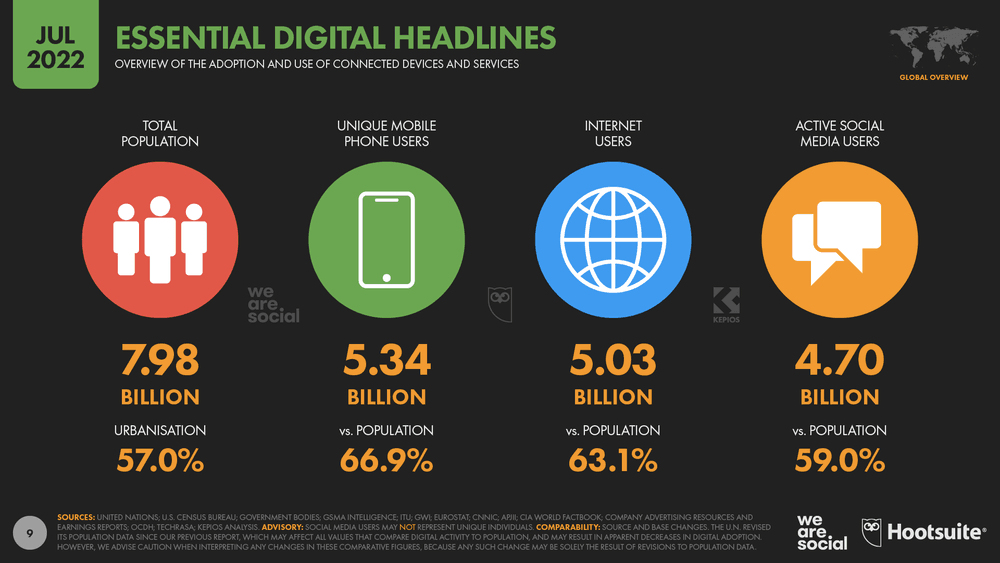
The Growing Digital Footprint
As the world becomes more interconnected, digital usage has skyrocketed. The Internet of Things (IoT), smartphones, cloud computing, and streaming services are just a few examples of the technology that fuels this digital age. But while these technologies bring us closer together and enhance our lives, they also have an environmental cost.
1. Energy Consumption
Every time we use a digital device—whether it’s a smartphone, laptop, or tablet—we are consuming energy. The energy required to power these devices doesn’t come from thin air; it has to be generated from natural resources, many of which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
According to a report by DataCamp, the energy demand of the global digital ecosystem is growing at an exponential rate. For example, data centers, which store the vast amounts of information we access every day, use significant amounts of energy to run servers and maintain their cooling systems. The result is a growing demand for electricity, much of which is still generated from fossil fuels like coal and natural gas, contributing to carbon emissions.
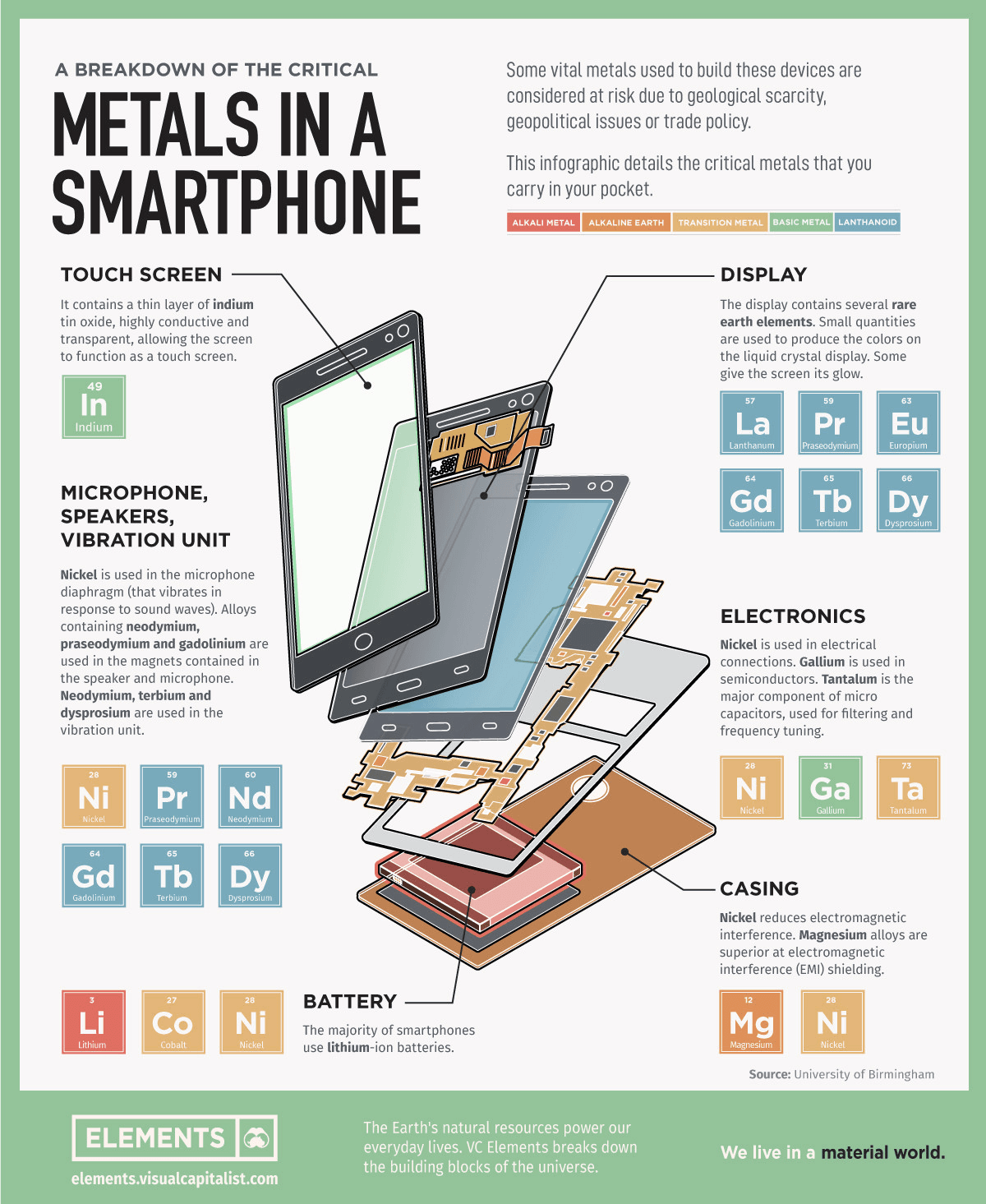
2. E-Waste
As digital devices become obsolete or break, they are often discarded. Electronic waste (e-waste) is one of the fastest-growing waste streams globally. According to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), around 53.6 million metric tons of e-waste were generated in 2019. The vast majority of this waste ends up in landfills, where it can leach harmful chemicals like lead, mercury, and cadmium into the soil and water, causing serious environmental damage.
Many digital devices also contain rare earth metals and precious materials that are difficult and expensive to recycle. As a result, many of these valuable resources are wasted when electronics are thrown away instead of being properly disposed of or recycled.
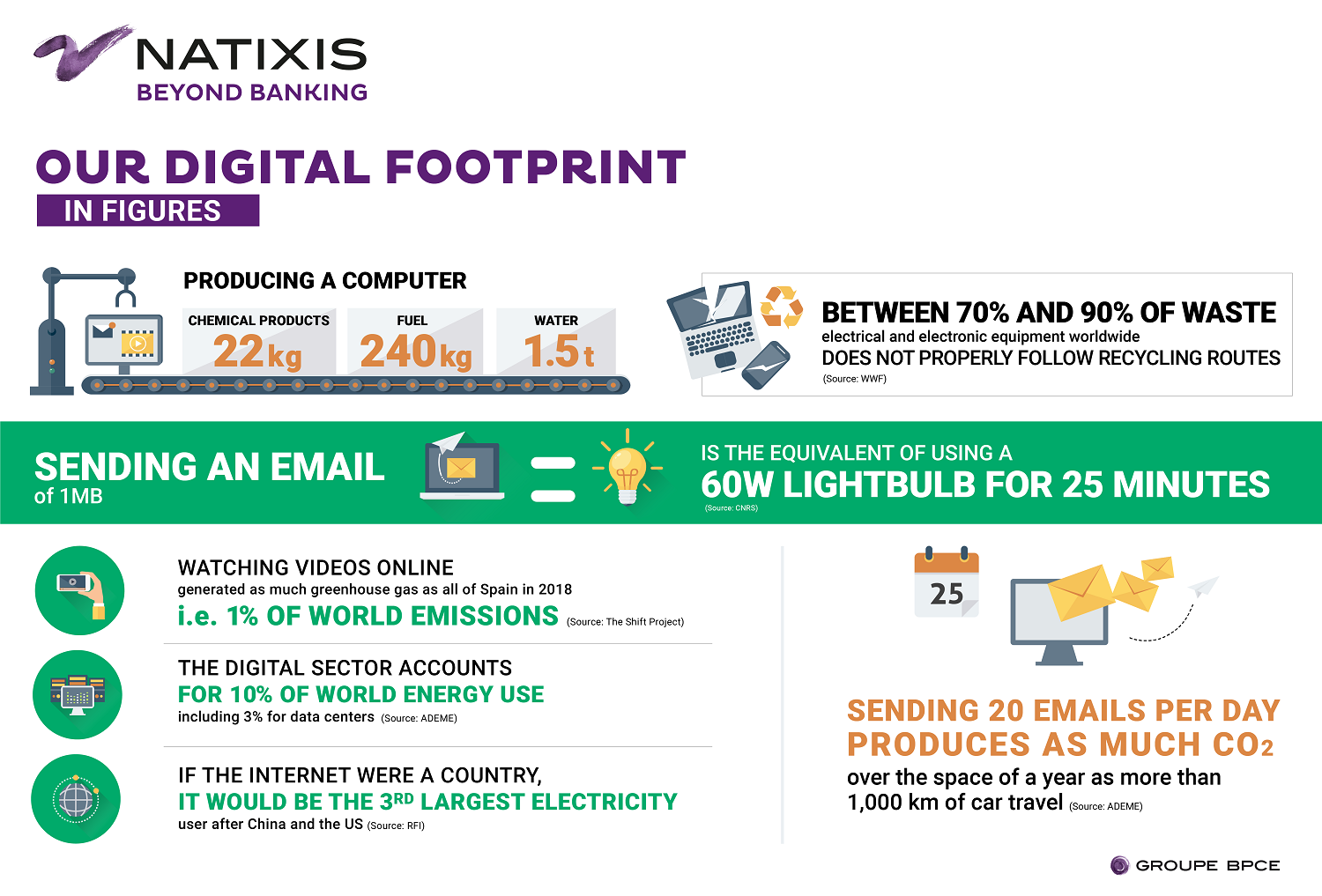
3. Carbon Emissions
The carbon footprint of digital technology is a major concern. The production and operation of devices, data centers, and networks release significant amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. A 2020 study by the Geneva Environment Network found that the digital sector accounts for around 4% of global CO2 emissions, a percentage comparable to the airline industry.
The growing use of cloud services and video streaming platforms further increases this footprint, as these services rely on large data centers powered by electricity. The environmental impact is amplified by the fact that many data centers are not yet powered by renewable energy sources.
The Role of Streaming and Data Consumption
One area where digital use has a significant environmental impact is in streaming services. The rise of video and music streaming platforms like Netflix, YouTube, and Spotify has changed the way we consume media, but it has also increased data consumption on a massive scale. Streaming video, for example, requires large amounts of data to be transferred and processed by data centers.
1. Streaming Video: A Data-Heavy Activity
When you stream a movie in HD or 4K, your device downloads and processes large video files, putting strain on both data centers and your local network. According to a study by Meduza, streaming a one-hour HD video can result in around 1.2 GB of data consumption, while 4K streaming can use over 7 GB per hour. The data required to stream high-definition content contributes significantly to the carbon footprint of the digital industry.
2. Cloud Computing
Cloud services like Google Drive, Dropbox, and Amazon Web Services are another major contributor to digital energy use. These services allow us to store vast amounts of data online, but the data must be stored and processed in data centers, which require significant amounts of energy to maintain. The growth of cloud computing further exacerbates the environmental impact of our digital lives.
The Environmental Cost of Digital Devices
The environmental cost of digital technology doesn’t stop at energy consumption and e-waste. The production of devices like smartphones, laptops, and tablets also has significant environmental implications. From mining for rare materials to the manufacturing process, the environmental cost of creating these products is often overlooked.
1. Mining for Rare Earth Metals
Digital devices contain a range of rare metals, including lithium, cobalt, and tantalum, which are crucial for battery production and other components. These metals are often mined in regions where environmental regulations are lax, leading to habitat destruction, pollution, and human rights abuses.
The extraction of these resources also consumes large amounts of water and energy, further contributing to environmental degradation. As demand for digital devices continues to rise, the pressure on these resources only increases, leading to further environmental damage.
2. The Carbon Footprint of Manufacturing
The manufacturing process for digital devices, from the creation of semiconductors to assembly, is energy-intensive. The production of smartphones alone accounts for a significant portion of the industry’s overall carbon emissions. According to the Carbon Trust, the carbon footprint of manufacturing a smartphone can range from 50 to 100 kg of CO2, depending on the device and production methods.
How to Reduce the Environmental Impact of Digital Use
While the environmental impact of digital technology is significant, there are steps we can take to reduce our carbon footprint and promote sustainability in the digital age.
1. Use Energy-Efficient Devices
When upgrading or purchasing new devices, consider choosing energy-efficient options. Look for devices with Energy Star ratings or those designed with sustainability in mind. Additionally, avoid constantly upgrading your devices; instead, try to extend the lifespan of your existing gadgets through repairs or by using them for longer.
2. Embrace Digital Minimalism
Adopting digital minimalism involves reducing the number of devices and digital services you use to minimize unnecessary energy consumption. By curating your digital life and focusing on only the most essential tools, you can help reduce your environmental footprint.
3. Opt for Green Hosting Services
If you’re involved in web hosting or cloud services, choose providers that use renewable energy to power their data centers. Many companies are moving towards green hosting solutions, which can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of digital services.
4. Recycle Electronics
Proper disposal and recycling of electronics is crucial for reducing e-waste. Many devices contain valuable materials that can be reused, reducing the need for mining and manufacturing new products. Make sure to dispose of old gadgets at certified e-waste recycling centers.
5. Limit Streaming
While streaming is convenient, it’s also one of the largest contributors to data consumption. Limit the amount of streaming you do, and consider downloading content to watch offline. Opt for lower-quality video streaming when possible, as this will reduce the amount of data required.
6. Support Eco-Friendly Brands
Support companies that prioritize sustainability in their production processes, from sourcing materials to packaging. Many brands now offer products made from recycled materials and focus on reducing waste throughout their manufacturing process.
Conclusion: A Greener Digital Future
The environmental impact of digital technology is significant, but it’s not too late to make a difference. By being more conscious of our digital consumption habits and adopting sustainable practices, we can reduce our carbon footprint and contribute to a greener future.
As digital technology continues to evolve, it’s important that we strike a balance between innovation and sustainability. By making informed choices—whether through reducing e-waste, embracing energy-efficient devices, or supporting green initiatives—we can ensure that our digital future does not come at the expense of the planet.

