Subscription-Based Shopping Models: The Future of Retail
In recent years, subscription-based shopping models have reshaped the retail landscape, offering consumers a convenient and personalized way to shop while providing businesses with a steady, predictable revenue stream. From beauty products and meal kits to streaming services and fashion, the subscription model has become an essential component of modern commerce. But what makes subscription shopping so appealing, and how can businesses leverage it to drive growth?
In this article, we’ll explore the subscription-based shopping model, its benefits, and how businesses can implement this model to enhance customer loyalty, streamline operations, and boost profitability.

What is a Subscription-Based Shopping Model?
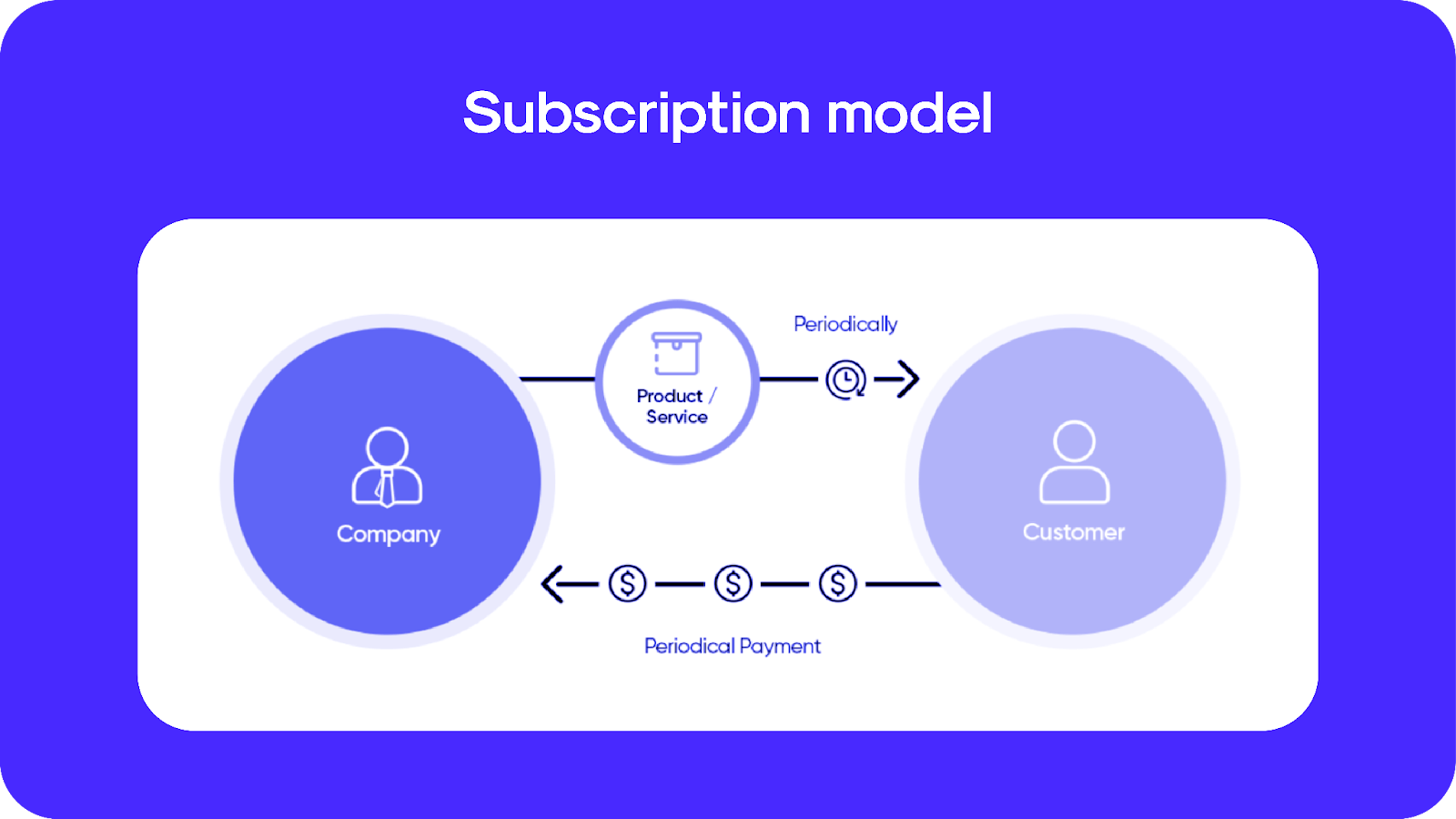
A subscription-based shopping model is a business model where customers pay a recurring fee—usually monthly, quarterly, or annually—in exchange for products or services delivered at regular intervals. Unlike traditional one-time purchases, subscriptions offer a continuous relationship between the customer and the business, often leading to greater customer retention and brand loyalty.
Key Characteristics of Subscription-Based Models:
- Recurring Revenue: Businesses earn a steady, predictable income stream.
- Personalization: Many subscription services offer customized products based on the customer’s preferences.
- Convenience: Subscriptions provide customers with regular deliveries, reducing the need to place individual orders.
- Flexibility: Customers can often adjust or cancel their subscriptions as needed.
The Benefits of Subscription-Based Shopping for Consumers
Subscription-based models offer a range of benefits for consumers, making them an attractive option for many. These benefits include:
1. Convenience
With subscription services, customers don’t have to repeatedly visit a website or store to make a purchase. Products are delivered automatically, saving time and effort. Whether it’s beauty products, groceries, or digital services, the subscription model ensures that customers never run out of their favorite items.
2. Cost Savings
Many subscription services offer discounts or perks for committing to a recurring plan. This can lead to significant cost savings for customers, especially if the service provides items they regularly use. For instance, meal kit subscriptions often offer better prices than buying ingredients separately from a store.
3. Personalization
Subscriptions can be highly personalized, offering customers tailored products based on their preferences or past purchases. Beauty box subscriptions, for example, might send personalized skincare or makeup products suited to a subscriber’s skin type or beauty preferences. This level of personalization adds value and makes customers feel special.
4. Exclusive Access
Subscribers often gain access to exclusive products, content, or experiences that are not available to non-subscribers. Whether it’s early access to a new product or limited edition items, subscription services can create a sense of exclusivity, making customers feel like part of a special group.
The Benefits of Subscription-Based Models for Businesses
While consumers benefit from the subscription model, businesses also stand to gain significantly. Some of the key advantages for businesses include:
1. Steady Cash Flow
Unlike traditional retail models that rely on sporadic purchases, subscription services provide a regular and predictable revenue stream. This steady cash flow can help businesses plan better, manage inventory more effectively, and even invest in future growth opportunities.
2. Customer Retention
Subscription models inherently encourage customer loyalty. Since customers commit to regular payments, they are less likely to churn compared to one-time buyers. Additionally, businesses can engage customers with regular updates, exclusive offers, and personalized content, strengthening the customer-business relationship over time.
3. Increased Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
The recurring nature of subscriptions means customers typically make more purchases over time, leading to a higher customer lifetime value (CLV). A customer who subscribes for a year will often generate more revenue than a customer who makes a one-off purchase.
4. Better Inventory Management
With a predictable number of subscribers, businesses can more accurately forecast demand and manage inventory. This reduces overstocking and understocking issues, optimizing the supply chain and minimizing waste.
Types of Subscription-Based Shopping Models
There are several types of subscription models, each tailored to different industries and customer needs. Below are the most common types:
1. Product Subscription Boxes
Product subscription boxes are one of the most popular types of subscription models. Customers receive a curated selection of products delivered to their door on a regular basis. These boxes can contain anything from beauty and grooming products to snacks, books, and pet supplies.
- Example: Birchbox offers personalized beauty boxes that include sample-sized skincare, makeup, and grooming products each month.
2. Service Subscriptions
Service subscriptions offer ongoing access to digital services, such as video streaming, music streaming, software-as-a-service (SaaS) products, or even educational content. These subscriptions provide a recurring service rather than physical goods.
- Example: Netflix and Spotify offer monthly subscriptions for streaming movies, shows, and music.
3. Meal Kits and Grocery Subscriptions
Meal kit subscriptions deliver fresh ingredients and recipes to customers’ doors, eliminating the need for grocery shopping. Customers can choose from various meal plans based on their dietary preferences, such as vegetarian, keto, or gluten-free.
- Example: Blue Apron and HelloFresh deliver pre-portioned ingredients for customers to cook meals at home.
4. Digital Content Subscriptions
This model provides access to premium digital content, such as news articles, magazines, or online courses. Customers subscribe to receive content at regular intervals.
- Example: The New York Times offers a subscription to access premium articles, while platforms like MasterClass provide educational content from industry experts.
5. Subscription Services for Physical Goods
Physical goods subscriptions allow customers to subscribe for regular deliveries of their favorite products. These could range from groceries and household items to health and wellness products.
- Example: Dollar Shave Club provides customers with a monthly subscription for razors and grooming products.
How to Build a Successful Subscription-Based Business
Launching a subscription-based business involves careful planning and strategy. To help you get started, here are some steps to consider:
1. Choose the Right Niche
To succeed in the subscription business, it’s essential to choose a niche that has demand and fits your brand. Whether it’s beauty products, health supplements, or pet toys, identify a market that aligns with customer interests and is underserved or underdeveloped.
2. Offer Value to Your Customers
A successful subscription model is built on offering value. Whether through convenience, personalization, or exclusivity, ensure your product or service solves a problem for customers and enhances their daily lives.
3. Optimize the Customer Experience
Provide an exceptional user experience from the moment customers sign up for the service. A seamless website, easy subscription management options, and prompt customer support are essential to creating a loyal customer base.
4. Pricing Strategy
Decide whether you want to offer a flat-rate subscription or tiered pricing based on the customer’s preferences or usage. Some businesses also offer discounts or incentives for longer subscription commitments.
5. Leverage Technology
Utilize tools and platforms that automate subscriptions, manage payments, and track customer data. Services like ReCharge, Cratejoy, and Bold Subscriptions can help streamline the subscription process.
Challenges of Subscription-Based Shopping Models
While the subscription model offers numerous benefits, it’s not without its challenges:
1. Customer Acquisition Costs
Attracting new subscribers can be expensive, especially when you factor in marketing, promotions, and discounts. However, once you acquire a customer, their recurring payments can make up for the initial investment.
2. Customer Retention
It’s crucial to maintain your subscriber base. Customers can easily cancel subscriptions if they don’t feel they’re receiving value. Providing engaging experiences and continuously offering value is key to retaining customers.
3. Over-Reliance on Subscribers
Subscription models depend on consistent customer engagement. If subscribers start canceling at a high rate, businesses can experience revenue fluctuations. To combat this, businesses need to continually innovate and offer value to keep subscribers happy.
Conclusion
The subscription-based shopping model is rapidly gaining traction across multiple industries. Its ability to provide businesses with predictable revenue, improve customer retention, and enhance customer loyalty makes it an appealing option for both startups and established companies.
Whether you’re in the beauty, food, entertainment, or software industry, embracing the subscription model can unlock new revenue opportunities and offer customers a more personalized, convenient shopping experience. As consumer preferences continue to evolve, businesses that adapt to this model will be well-positioned for long-term success.
FAQs
1. What is the biggest advantage of a subscription-based model?
The biggest advantage is the steady, recurring revenue it offers. Businesses can rely on predictable cash flow, while customers enjoy the convenience of regular deliveries.
2. How can I ensure my subscription service stands out?
Focus on offering personalized products, creating exclusive experiences, and delivering exceptional customer service.
3. Can I cancel a subscription at any time?
Yes, most subscription services offer the flexibility to cancel or modify subscriptions at any time, depending on the terms and conditions of the service.

