Solar Energy Explained: The Power of the Sun
In today’s world, solar energy has become a central focus in the global effort to transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. As the planet faces the challenges of climate change, rising energy costs, and the depletion of fossil fuel resources, solar energy stands out as one of the most effective and accessible solutions. This article will dive into what solar energy is, how it works, its benefits, and how it’s revolutionizing the energy landscape.
What is Solar Energy?
Solar energy is the energy harnessed from the sun’s radiation. The sun provides an enormous amount of energy—more than enough to meet the world’s needs—so it’s a renewable, clean source of power. Solar energy can be converted into electricity or heat, which can then be used for a variety of applications, including heating homes, powering appliances, and even driving vehicles.
Solar energy is classified into two main types:
– Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Energy: This is the most common type, where sunlight is directly converted into electricity through solar panels.
– Concentrated Solar Power (CSP): This method uses mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight onto a small area to generate heat, which is then used to produce electricity.
How Does Solar Energy Work?
At its core, solar energy works by capturing sunlight and converting it into a usable form of energy. This process varies slightly depending on the technology used, but the fundamental principles remain the same.
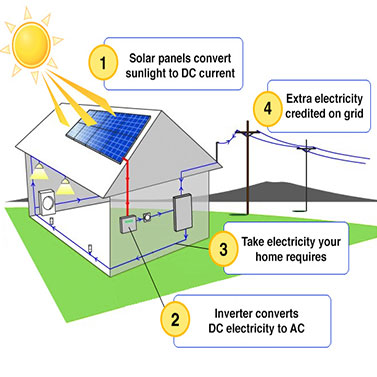
1. Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Panels
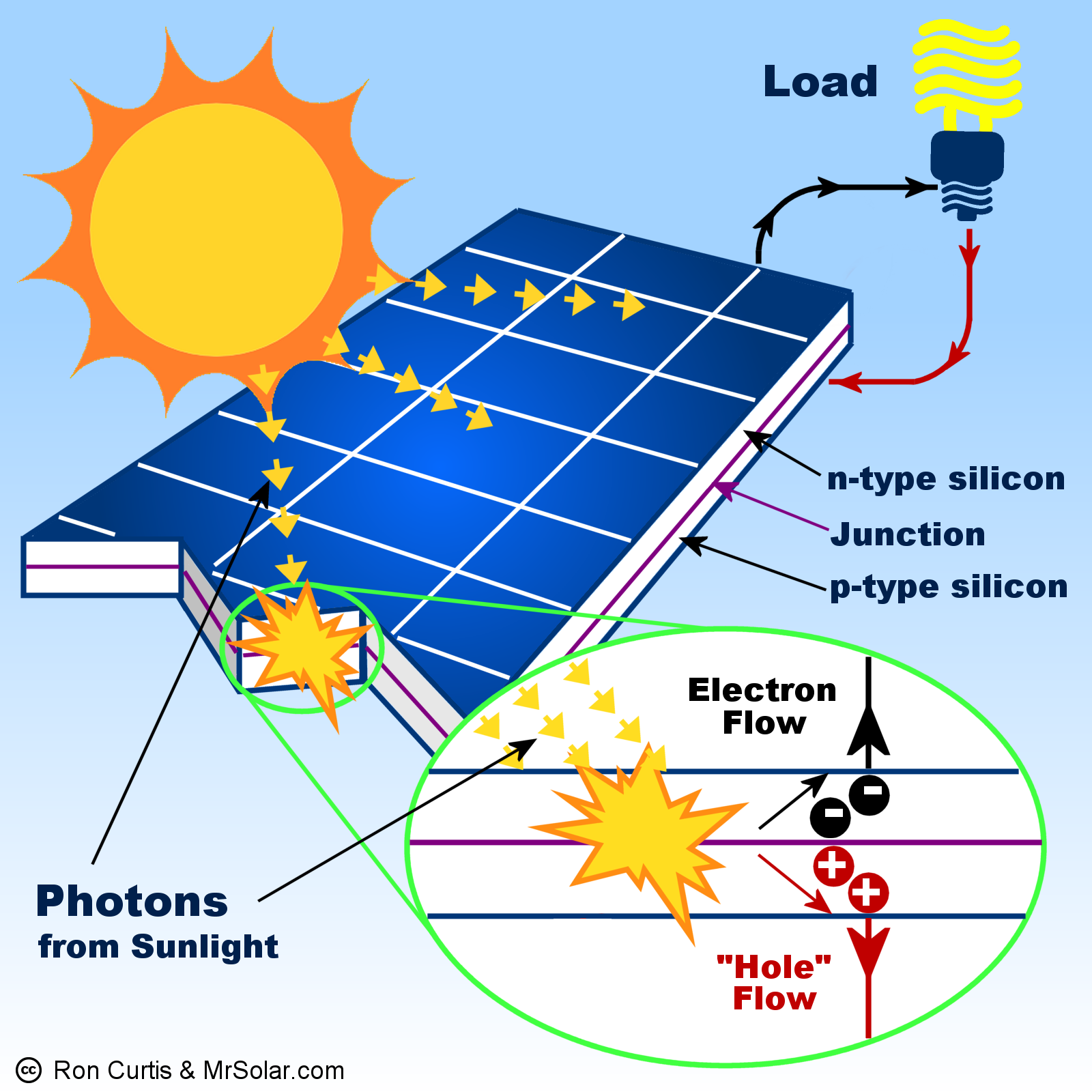
Photovoltaic solar panels are the most widely used technology to harness solar energy. These panels are made up of solar cells, usually made from silicon, which convert sunlight directly into electricity. Here’s how it works:
- Solar Cells Absorb Sunlight: When sunlight hits a solar panel, photons (light particles) are absorbed by the solar cells, which excites the electrons within the cells.
- Electron Movement Creates Electricity: The movement of these electrons creates an electric current, which can then be harnessed and used to power homes, buildings, or even electric grids.
- Inverter Converts DC to AC: The electricity generated by solar panels is direct current (DC), but most homes and appliances use alternating current (AC). A solar inverter converts the DC electricity into usable AC electricity.
2. Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
In CSP systems, large mirrors or lenses are used to focus sunlight onto a receiver. The concentrated sunlight heats up the receiver, which contains a fluid that absorbs the heat. This fluid is then used to generate steam, which powers a turbine that produces electricity.
CSP systems are typically used in large-scale solar power plants located in sunny regions, as they require vast amounts of sunlight to generate significant amounts of energy.
3. Solar Thermal Energy Systems
Another method of using solar energy is through solar thermal systems, which capture the heat from the sun to directly heat water or air. These systems are often used in residential and commercial applications to provide hot water or space heating.
The Benefits of Solar Energy
Solar energy offers numerous benefits, making it one of the most promising alternatives to traditional fossil fuels. Here are some key advantages:
1. Renewable and Sustainable
Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy is renewable, meaning it will not run out for billions of years. As long as the sun is shining, we can harness its energy, making it an inexhaustible source of power.
2. Environmentally Friendly
Solar energy is clean and produces zero emissions. By switching to solar power, we can significantly reduce our carbon footprint and minimize the harmful effects of fossil fuels on the environment. This is a critical step in the fight against climate change and the reduction of air pollution.
3. Reduces Energy Bills
While the initial installation of solar panels can be costly, over time, they can significantly reduce electricity bills. Once the system is set up, sunlight is free, and the energy you generate from your panels can either be used in your home or sold back to the grid in some regions. This means long-term savings and energy independence.
4. Low Maintenance Costs
Solar energy systems have low maintenance requirements. Once installed, solar panels have no moving parts, which means fewer opportunities for wear and tear. With periodic cleaning and inspections, solar panels can last for 25 years or more.
5. Energy Independence
By generating your own solar power, you reduce your reliance on the grid and fossil fuels. This is especially beneficial during power outages or in areas with unstable energy supplies.
Solar Energy Applications
Solar energy is versatile and can be used for various applications:
1. Residential Solar Energy
Homeowners can install solar panels on their roofs to generate electricity for their homes. This is often done in combination with solar batteries, which store excess energy for use at night or during cloudy periods.
2. Commercial Solar Power
Many businesses are adopting solar energy to reduce operating costs and meet sustainability goals. Large warehouses, factories, and office buildings can install solar panels to power their operations, reducing their electricity costs and carbon footprint.
3. Solar-Powered Vehicles
Solar energy is being used to power electric vehicles (EVs). While solar-powered cars are still in their infancy, solar panels can be used to charge EV batteries, offering a cleaner alternative to traditional charging methods.
4. Solar Farms
Large-scale solar farms consist of thousands of solar panels spread across large areas of land. These farms generate massive amounts of electricity, which is then fed into the electric grid to provide power to thousands of homes and businesses.
The Future of Solar Energy
The future of solar energy is incredibly promising, with ongoing advancements in technology that are making solar power more efficient, affordable, and accessible. Some exciting developments include:
1. Improved Efficiency
Solar panel efficiency is steadily increasing. New materials, such as perovskite and multi-junction cells, are being developed to increase the amount of sunlight that can be converted into electricity, making solar energy even more efficient.
2. Solar Energy Storage
One of the challenges of solar power is its intermittency—the sun doesn’t always shine when electricity is needed. However, advancements in battery storage technology, such as lithium-ion batteries, are improving, allowing excess solar energy to be stored and used when demand is higher.
3. Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
Rather than just mounting solar panels on roofs, Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) integrate solar cells directly into building materials, such as windows and walls. This approach allows for a more seamless integration of solar energy into urban environments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How do solar panels work?
Solar panels work by converting sunlight into electricity. Photovoltaic cells within the panels absorb sunlight and release electrons, creating an electric current that is then used to power homes or businesses.
2. Is solar energy free?
Once solar panels are installed, the sunlight that powers them is free. However, there is an initial investment for purchasing and installing the solar panels and the associated equipment.
3. How much do solar panels cost?
The cost of solar panels can vary depending on factors like the size of the system, the type of panels, and installation fees. On average, residential systems can cost anywhere from $10,000 to $30,000, with the potential for long-term savings.
4. What are the environmental benefits of solar energy?
Solar energy produces zero emissions, reducing air pollution and mitigating the effects of climate change. It is also a renewable resource that does not deplete natural resources like fossil fuels.
Conclusion
Solar energy is undoubtedly one of the most exciting and accessible renewable energy sources available today. It is clean, sustainable, and versatile, with the potential to meet a significant portion of the world’s energy needs. As technology continues to improve and the cost of installation decreases, solar power is set to play an even more crucial role in the global transition to a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.

By harnessing the power of the sun, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, combat climate change, and move toward a more sustainable energy future. Whether through home installations, commercial applications, or large-scale solar farms, solar energy is shaping the future of energy generation—one sunny day at a time.

