Picking and Packing Strategies: Optimizing Your Warehouse Operations
In today’s fast-paced retail and logistics environments, the picking and packing process is crucial for maintaining efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. These processes are fundamental to order fulfillment, directly affecting the speed and accuracy with which products reach customers. A well-organized picking and packing strategy can lead to reduced operational costs, faster delivery times, and increased customer loyalty.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the different picking and packing methods, their benefits, and how to choose the best strategies for your warehouse. We’ll also explore how modern technologies can improve your warehouse operations, making them more efficient and scalable.

What is Picking and Packing?
Picking and packing are two key processes in the order fulfillment cycle. Here’s a brief breakdown of each:
- Picking: The process of retrieving products from their storage locations within the warehouse to fulfill an order.
- Packing: The process of preparing picked products for shipment, including boxing, labeling, and securing items for delivery.
Both processes must be handled efficiently to minimize errors, reduce costs, and ensure timely delivery to customers. Let’s explore the most popular picking and packing strategies in more detail.
Popular Picking Strategies
The picking method you choose will depend on the size of your warehouse, the types of products you store, and the volume of orders you process. Below are some common picking strategies:
1. Single Order Picking
Single order picking is the simplest method, where an employee picks all the items for a single order at once. This strategy is most effective for warehouses with low order volumes or when the items in each order are scattered throughout the warehouse.
Pros:
- Simple to implement: Easy to set up and manage.
- Efficient for small orders: Best suited for single-item or low-volume orders.
Cons:
- Not scalable: Can become inefficient as order volume increases.
- Higher labor costs: Requires more time to pick multiple items for different orders.
2. Batch Picking
Batch picking involves collecting items for multiple orders in one go. Warehouse employees pick the same item for multiple orders simultaneously, reducing the time spent traveling back and forth across the warehouse.
Pros:
- Time savings: Employees make fewer trips around the warehouse.
- Better suited for high order volume: Ideal for warehouses processing large quantities of similar items.
Cons:
- Complexity: Requires accurate tracking to ensure that items are correctly allocated to the right order.
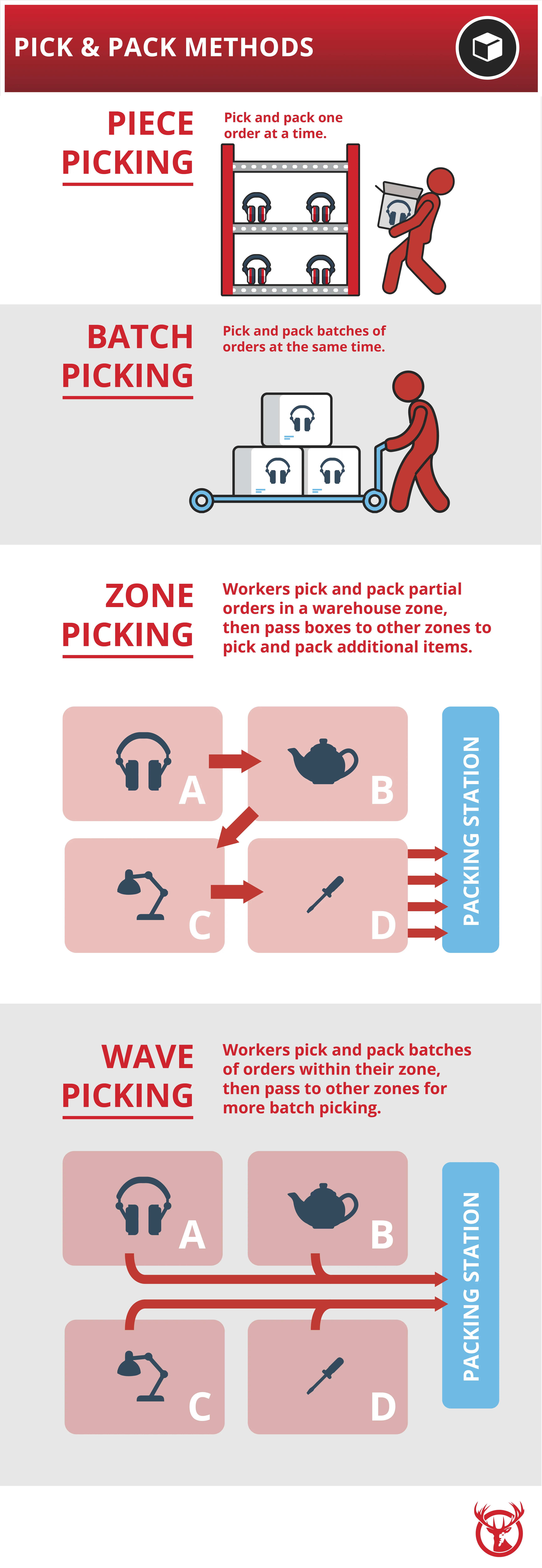
3. Zone Picking
In zone picking, the warehouse is divided into different zones, each managed by a picker. When an order comes in, the items are picked from different zones, either by the same or different employees. Once the order is fully picked, it is passed to the packing station.
Pros:
- Reduced walking time: Pickers only need to navigate their designated zones.
- Ideal for larger warehouses: Helps manage high-volume or diverse inventory across various zones.
Cons:
- Requires coordination: Needs robust software to track orders across zones and ensure all items are picked.
4. Wave Picking
Wave picking combines batch and zone picking. Orders are grouped into waves based on specific criteria, such as priority or shipping method. Employees pick items for all orders in a wave before moving to the next wave, reducing idle time.
Pros:
- Increased productivity: Reduces unnecessary waiting time between order fulfillment tasks.
- Flexible: Works well for orders with varying priorities and delivery deadlines.
Cons:
- Requires more planning: Must be carefully coordinated to ensure orders are picked on time.
5. Automated Picking Systems
Automated picking systems use robots, conveyors, and artificial intelligence (AI) to pick items. This method is ideal for businesses with very high order volumes or those that need to maintain extremely high picking accuracy.
Pros:
- Speed and efficiency: Robots can operate around the clock, increasing throughput.
- Accuracy: AI ensures that items are picked correctly, minimizing errors.
Cons:
- High initial cost: Requires a significant investment in technology and infrastructure.
- Not suitable for all types of products: Best for standardized and non-perishable items.
Common Packing Strategies
Once items are picked, the next crucial step is packing. There are several packing strategies to consider, depending on your warehouse’s specific needs:
1. Manual Packing
Manual packing is the traditional method where employees pack each order by hand. It’s often used in smaller warehouses or when packing requires custom handling.
Pros:
- Flexibility: Allows for custom packaging and handling of fragile or specialty items.
- Low initial investment: No significant technology or infrastructure required.
Cons:
- Slower processing time: Can become inefficient with high order volumes.
- Higher labor costs: Requires more workers and can lead to higher operational costs.
2. Automated Packing Systems
Automated packing systems use machines to pack orders quickly and accurately. These systems can weigh, label, and pack products automatically, reducing the need for human labor.
Pros:
- Speed: Can pack orders much faster than manual systems.
- Consistency: Ensures each package is packed according to preset guidelines.
Cons:
- High upfront costs: Automation requires a significant initial investment.
- Limited flexibility: Automated systems may not be suitable for handling items that require special attention.

3. Batch Packing
Batch packing involves grouping multiple orders together to be packed at the same time. This strategy is efficient when orders contain similar items or need to be shipped using the same method.
Pros:
- Improved efficiency: Allows employees to pack several orders simultaneously.
- Reduces errors: Grouping orders together minimizes the chances of packing mistakes.
Cons:
- Not ideal for small, custom orders: Batch packing works best when orders are similar in nature.
4. Kitting
Kitting involves grouping several individual items into a single package for shipping. This strategy is commonly used when customers purchase bundles or gift sets that contain multiple items.
Pros:
- Simplified fulfillment: Customers receive a complete package, reducing the need for multiple shipments.
- Increased sales: Offering pre-packaged sets or bundles can encourage higher sales.
Cons:
- Complex inventory management: Requires careful tracking of bundled items to ensure stock levels remain accurate.
How to Choose the Right Picking and Packing Strategy
Choosing the right strategy for your warehouse depends on several factors, including your order volume, product types, and available resources. Here are some key considerations:
- Order volume: High-volume warehouses benefit from batch or zone picking, while small operations may do well with single-order picking.
- Product type: Fragile or custom items may require manual packing or specialized packing methods.
- Technology investment: If your business can afford automation, robotic systems and automated packing solutions can drastically increase efficiency.
Technology’s Role in Optimizing Picking and Packing
In recent years, technology has played a pivotal role in improving picking and packing strategies. Advanced Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) integrate picking and packing processes with real-time data, helping to track inventory levels, streamline workflows, and reduce errors. Additionally, technologies like RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and AI help improve accuracy and optimize inventory management.
For businesses considering automation, systems like Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and robotic pickers can reduce labor costs, increase picking speeds, and enhance accuracy in both picking and packing stages.
Conclusion
Optimizing your picking and packing strategies is essential to running a successful warehouse operation. Whether you choose manual picking, batch picking, or a more automated solution, it’s crucial to tailor your approach to your specific business needs. By investing in the right technologies, continuously refining your processes, and training your staff, you can streamline your warehouse operations and enhance the customer experience.
To learn more about efficient picking and packing methods, check out these helpful resources:

