Lean Startup Methodology: A Comprehensive Guide to Building Successful Startups
The Lean Startup Methodology has transformed how entrepreneurs approach building their businesses in today’s fast-paced, uncertain environment. This approach emphasizes validated learning, rapid experimentation, and customer feedback, enabling startups to minimize risk and maximize success.
What is Lean Startup Methodology?
Lean Startup is a systematic, scientific approach to creating and managing successful startups. Developed by Eric Ries, it draws from lean manufacturing principles, focusing on efficiency and the elimination of waste. Instead of traditional business plans, the Lean Startup Methodology encourages entrepreneurs to test their assumptions continuously and pivot based on real customer feedback.
Origins of Lean Startup
The roots of the Lean Startup Methodology can be traced back to Toyota’s production system, which emphasized efficiency and reducing waste in manufacturing. Eric Ries adapted these principles to the startup environment, advocating for a flexible, iterative approach that allows businesses to adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
Key Principles of Lean Startup Methodology
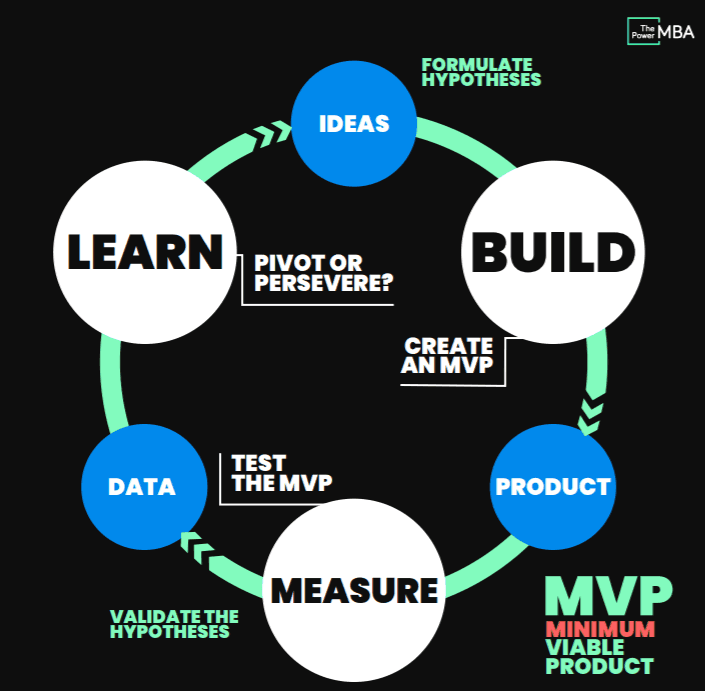
- Build-Measure-Learn: The core cycle of the Lean Startup approach, emphasizing rapid prototyping and customer feedback.
- Minimum Viable Product (MVP): Developing a product with just enough features to satisfy early adopters and gather feedback.
- Validated Learning: Learning through systematic experimentation to validate assumptions about the market and product.
The Lean Startup Process
The Lean Startup process is a cycle of experimentation that helps entrepreneurs refine their ideas based on real-world data. This process consists of several key steps:
Step 1: Ideation and Hypothesis Formation
Every successful startup begins with an idea. However, it’s crucial to transform that idea into testable hypotheses. What problem does your product solve? Who is your target audience? This phase involves conducting market research to identify gaps and opportunities.
Step 2: Build-Measure-Learn Cycle
The essence of the Lean Startup Methodology lies in the Build-Measure-Learn cycle:
- Build: Create your Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to test your hypotheses. The MVP should include only the essential features needed to address the problem you aim to solve.
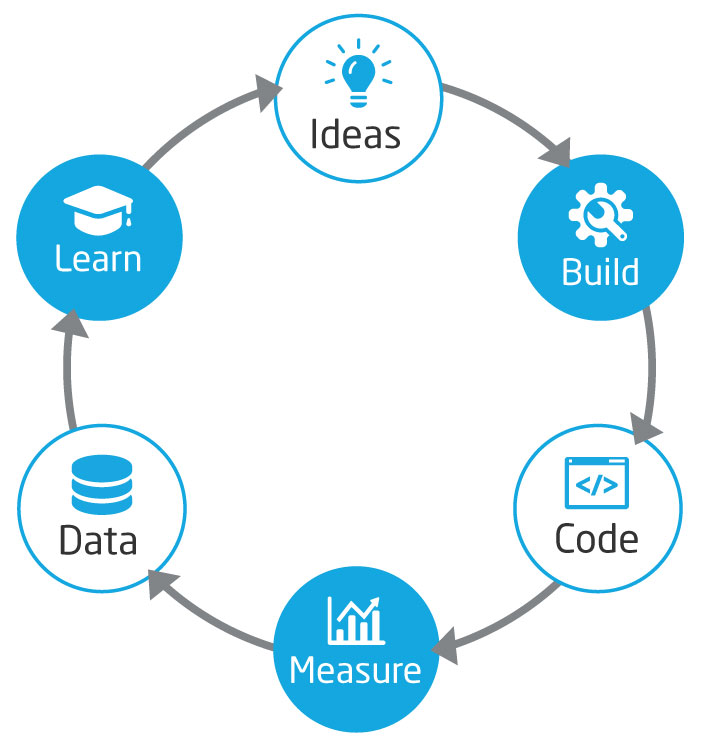
- Measure: Once your MVP is launched, collect data on how users interact with your product. This phase involves analyzing metrics that matter—such as user engagement, retention rates, and customer feedback.
-
Learn: Based on the data collected, you can validate or invalidate your hypotheses. This feedback loop is crucial for understanding what works and what doesn’t, allowing you to make informed decisions.
Building the Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Creating an MVP is essential for startups aiming to minimize waste and maximize learning. Your MVP should be a stripped-down version of your product that captures the essence of your value proposition. This allows you to test assumptions with minimal investment.
Measuring Success: Key Metrics and KPIs
Identifying the right metrics to evaluate your MVP is critical. Common Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for startups include:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
- Churn Rate
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Each of these metrics provides insights into how well your product meets customer needs and its potential for growth.
Learning and Iteration: Pivot or Persevere
After analyzing the data, startups face a crucial decision: pivot or persevere. If your hypotheses are validated, continue on your current path, iterating and enhancing your product. However, if your data indicates that your assumptions are incorrect, it may be time to pivot—change your strategy to better meet market demands.
Tools and Techniques in Lean Startup
Various tools and techniques can help startups implement the Lean Startup Methodology effectively:
Customer Development: Understanding Your Customers
Customer development is an integral part of the Lean Startup approach. Engaging directly with your target audience through interviews, surveys, and focus groups can help you uncover valuable insights about their needs and preferences.
Agile Development: Adapting to Change
Utilizing Agile development practices allows teams to adapt quickly to feedback and changes in the market. By breaking projects into smaller, manageable increments, businesses can respond to customer needs more effectively.
Validated Learning: Ensuring Product-Market Fit
The ultimate goal of the Lean Startup Methodology is to achieve product-market fit—where your product effectively meets customer demands. Regularly testing your product and gathering customer feedback will help you refine your offering until it aligns perfectly with market needs.
Benefits of Lean Startup Methodology
Implementing the Lean Startup Methodology offers numerous advantages for entrepreneurs:
- Cost-Effectiveness and Resource Efficiency: By focusing on validated learning and MVPs, startups can reduce wasted resources and minimize financial risk.
- Faster Time to Market: Rapid prototyping and testing allow businesses to bring their products to market quicker, gaining a competitive edge.
- Enhanced Customer Focus: Continuous feedback loops ensure that product development is aligned with customer needs, leading to greater satisfaction and loyalty.
Challenges and Misconceptions
Despite its numerous benefits, the Lean Startup Methodology is not without challenges.
Common Misconceptions about Lean Startup
One common misconception is that the Lean Startup approach is solely about speed. While quick iterations are essential, quality should never be compromised.
Potential Challenges in Implementation
Implementing the Lean Startup methodology can be challenging for teams accustomed to traditional business models. Resistance to change and a lack of understanding of the methodology can hinder progress.
In the second half of this article, we will explore real-world examples of companies that successfully applied the Lean Startup Methodology, provide insights into overcoming common challenges, and answer frequently asked questions to help you implement these strategies effectively. Stay tuned!
Real-World Examples of Lean Startup Methodology
Understanding how the Lean Startup Methodology works in practice can provide invaluable insights for entrepreneurs. Here are some notable examples of companies that have successfully implemented these principles:
1. Dropbox
Dropbox, a cloud storage service, is a classic example of the Lean Startup approach. Before building the full product, Dropbox created a simple video demo of its concept. This MVP allowed the founders to gauge interest and collect user feedback before investing in a complete product. As a result, they amassed a significant waiting list, validating their idea and ensuring they built a product that users actually wanted.

2. Zappos
Zappos, an online shoe retailer, started with a very lean model. The founder, Nick Swinmurn, took pictures of shoes in local stores and posted them online. When customers ordered shoes, he would purchase them from the stores, fulfilling the orders manually. This approach allowed Zappos to validate the demand for online shoe sales without investing heavily in inventory upfront.
3. Airbnb
Airbnb began as a simple MVP, renting out a single apartment during a convention in San Francisco. The founders gathered data from their initial customers, using feedback to iterate on their platform and services. Today, Airbnb is a global giant in the hospitality industry, demonstrating the power of validating ideas early and often.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Lean Startup
While the Lean Startup Methodology offers numerous benefits, startups often face challenges during implementation. Here are strategies to navigate these hurdles:
1. Resistance to Change
Many teams are accustomed to traditional methodologies and may resist adopting a new approach. To mitigate this, ensure clear communication about the benefits of the Lean Startup Methodology and involve team members in the transition process. Offer training sessions to familiarize them with new tools and processes.
2. Misinterpreting MVP
A common mistake is misunderstanding what constitutes an MVP. Remember, an MVP should deliver enough value to users to validate your hypothesis without being a fully developed product. Focus on core features that address customer pain points rather than trying to create a perfect solution.
3. Insufficient Data Analysis
Startups may struggle with analyzing data effectively. Establish a clear framework for tracking metrics, and regularly review this data to inform your next steps. Utilizing tools like Google Analytics or Mixpanel can help streamline this process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the primary goal of the Lean Startup Methodology?
The primary goal is to reduce the time it takes to validate ideas and bring a successful product to market by utilizing continuous feedback and iterative processes.
Q2: How do I know if my MVP is successful?
An MVP is considered successful if it provides enough customer insights to validate your assumptions and if you can identify clear next steps for further development.
Q3: Can established companies benefit from Lean Startup principles?
Absolutely! Established companies can adopt Lean Startup principles to innovate and remain competitive by continuously testing and iterating on their products or services.
Q4: What are the key metrics I should track?
Key metrics include Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), churn rate, and user engagement metrics. These KPIs will help you gauge the success of your MVP and overall business model.
Q5: How often should I iterate my product?
Iteration should occur as frequently as necessary based on customer feedback and data analysis. The goal is to be responsive to user needs and market changes.
Conclusion
The Lean Startup Methodology empowers entrepreneurs to navigate uncertainty and innovate effectively. By focusing on validated learning, rapid experimentation, and customer feedback, startups can minimize risk and maximize the potential for success. Implementing this approach requires commitment and flexibility, but the rewards—a product that genuinely meets customer needs and a business poised for growth—are well worth the effort.
Incorporating the Lean Startup principles into your entrepreneurial journey can provide a robust framework for turning your ideas into successful ventures. As you embark on this path, remember that continuous learning and adaptation are key to thriving in today’s dynamic market landscape.
For further reading, consider exploring The Lean Startup website for additional resources and community support. Also, be sure to check out articles on customer development to deepen your understanding of how to engage effectively with your target audience.