Competitors and Industry Influence: Navigating the Market Landscape
In today’s fast-paced and competitive market, understanding the impact of competitors and industry influences is crucial for businesses aiming to stay ahead of the curve. Whether you’re an established company or a new entrant, comprehending the competitive dynamics that shape your industry can help you make informed decisions, innovate, and maintain profitability.
In this article, we’ll explore how competitors influence the industry, the different types of competitive forces, and the strategies companies can use to navigate a competitive landscape. We’ll also look at how market demand, economic trends, and other factors affect competition and industry behavior.
Understanding the competitive landscape is key to achieving long-term success.
1. The Role of Competitors in Shaping Market Demand
Competition plays a central role in shaping market demand and influencing business behavior. Competitors not only drive pricing strategies but also push innovation, product development, and marketing tactics. Below are some key ways in which competitors affect demand:
Price Sensitivity and Consumer Choices
- Price wars: When competitors aggressively lower prices, they can spark price wars, leading to a reduction in overall market prices. While this benefits consumers, it can put pressure on companies’ profit margins.
- Consumer preferences: Competitors often influence consumer preferences through their marketing strategies, product offerings, and value propositions. As consumers have more choices, they become more selective, driving demand for better products at competitive prices.
Innovation and Product Differentiation
In a competitive industry, companies are forced to innovate in order to maintain or grow their market share. This creates a feedback loop where competitors continuously improve their products and services to meet evolving consumer expectations.
- Innovation cycles: Competitors’ innovations can disrupt the market and force other players to adapt or lose relevance.
- Differentiation: Companies distinguish themselves by offering unique features, customer service, or branding that appeals to their target audience. This encourages brand loyalty and shapes consumer buying behavior.
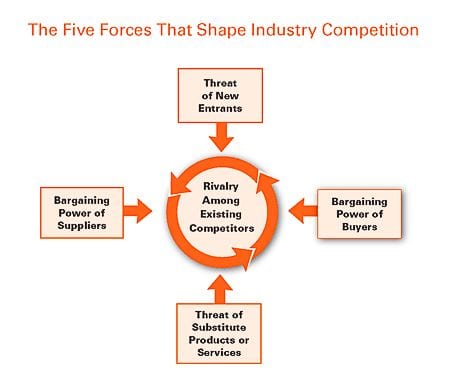
2. Types of Competition in Industry
Competition can take several forms, each with its own influence on the market. Understanding these competitive forces is essential for businesses to craft effective strategies.
Direct Competition
Direct competitors are companies that offer similar products or services within the same market. This is the most straightforward type of competition, where businesses go head-to-head in offering comparable value to customers.
- Example: In the smartphone industry, companies like Apple and Samsung are direct competitors. Both companies offer similar features in their smartphones, with the primary differentiation being their ecosystem and brand loyalty.
Indirect Competition
Indirect competitors are businesses that offer products or services that serve as substitutes for what you offer. While these companies may not be in the same market, they can still draw potential customers away.
- Example: In the beverage industry, companies like Coca-Cola and Pepsi compete directly with each other. However, they may also face indirect competition from health drinks, bottled water brands, or even coffee retailers.
Potential Entrants (Barriers to Entry)
New entrants can pose a threat to existing businesses, particularly if they have access to innovative technologies or disruptive business models. Barriers to entry—such as capital requirements, economies of scale, and brand loyalty—can protect established companies from new competition.
- Example: The tech industry often sees new players entering with fresh ideas or technologies. For instance, startups focusing on artificial intelligence (AI) may challenge established tech giants in the future.
Substitute Products
Companies producing substitute products can influence market demand by offering alternatives that meet the same need. The presence of substitutes can limit pricing power and force companies to offer better value.
- Example: In the transportation sector, the rise of electric scooters and ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft have become substitutes for traditional taxi services.
3. External Forces and Industry Influence
While competitors are a critical component of the market, several external forces also shape the competitive landscape. These forces can impact market demand, company strategies, and overall industry growth.
Economic Factors
The state of the economy plays a significant role in determining market conditions. A booming economy may result in higher demand for products and services, while economic downturns can force companies to reduce costs, innovate, or adopt more aggressive marketing tactics.
- Example: During periods of economic expansion, consumers tend to spend more, leading to higher demand for luxury goods and services. In contrast, during a recession, price sensitivity increases, and consumers shift to more affordable alternatives.
Technological Advancements
Technological developments often change the competitive landscape by creating new opportunities or rendering older products obsolete. Companies that can adapt quickly to new technologies often gain a competitive advantage.
- Example: The rise of cloud computing disrupted traditional IT models, forcing companies to either adopt the cloud or risk falling behind competitors who did.
Regulatory Environment
Government regulations and policies can shape industry dynamics by enforcing rules on pricing, product standards, advertising, and environmental practices. Companies must stay compliant to avoid penalties, but regulations can also influence competition by favoring certain industry players.
- Example: The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has affected how companies handle customer data, which has forced many companies to adapt their marketing strategies and operational models.
Social and Cultural Trends
Consumer behaviors and societal shifts also influence demand and competition. For example, as consumers become more conscious of sustainability, companies in various industries may find that eco-friendly products are a key differentiator in their competitive strategies.
- Example: The rise of the plant-based food industry reflects changing consumer preferences toward healthier and more sustainable eating habits.
4. Strategies to Navigate Competitive Pressure
Given the intense competition and ever-changing external forces, businesses must adopt strategies to maintain a competitive edge and sustain growth. Below are some effective strategies companies can employ:
Focus on Innovation and R&D
Investing in research and development (R&D) is a key strategy for businesses to stay ahead of competitors. Continuous innovation ensures that companies can offer new products or enhance existing ones to meet consumer needs.
- Example: Companies like Apple and Tesla are known for their relentless focus on R&D, which enables them to deliver cutting-edge products year after year.
Customer-Centric Marketing
In a competitive environment, understanding and meeting customer needs is essential. By focusing on personalized experiences, businesses can build loyalty and attract customers even in highly competitive markets.
- Example: Amazon uses data-driven marketing to deliver tailored product recommendations, ensuring that customers have a seamless shopping experience.
Cost Leadership and Operational Efficiency
Companies that can offer products at lower prices without sacrificing quality often gain an advantage in price-sensitive markets. Achieving cost leadership through operational efficiency and economies of scale is a tried-and-tested strategy.
- Example: Walmart’s ability to offer low prices through its efficient supply chain and vast distribution network has made it a leader in the retail industry.
5. FAQs About Competitors and Industry Influence
Q1: How do competitors influence product prices?
Competitors impact product prices through price wars, discounting, and by setting a pricing benchmark in the market. When one company lowers its prices, others often follow suit, affecting overall market pricing.
Q2: How can new entrants affect an established business?
New entrants can disrupt the market by offering innovative products, better prices, or improved services. Established businesses may need to adapt quickly to maintain market share.
Q3: What role does technology play in competition?
Technology is a significant driver of competition. Companies that leverage new technologies often gain a competitive edge, while others may fall behind if they fail to adapt.
Q4: What strategies help businesses deal with intense competition?
To deal with intense competition, businesses can focus on innovation, cost leadership, and customer-centric marketing to differentiate themselves in the market.
Conclusion
Navigating competition and industry influence is vital for businesses looking to thrive in today’s ever-evolving market. By understanding the competitive forces at play and employing strategies like innovation, cost management, and customer focus, companies can maintain a competitive advantage and foster sustainable growth.
As markets continue to change, staying informed and adaptable is the key to success in a competitive landscape. For more insights on navigating competition, check out resources like Harvard Business Review.

