Community Solar Projects: Powering the Future of Renewable Energy
The transition to renewable energy is crucial in tackling the climate crisis and ensuring a sustainable future. One of the most promising developments in the solar energy sector is the rise of community solar projects. These projects provide an opportunity for individuals, businesses, and communities to harness the power of the sun without having to install solar panels on their own property. In this article, we will explore the concept of community solar, how it works, its benefits, and why it is a game-changer for clean energy accessibility.
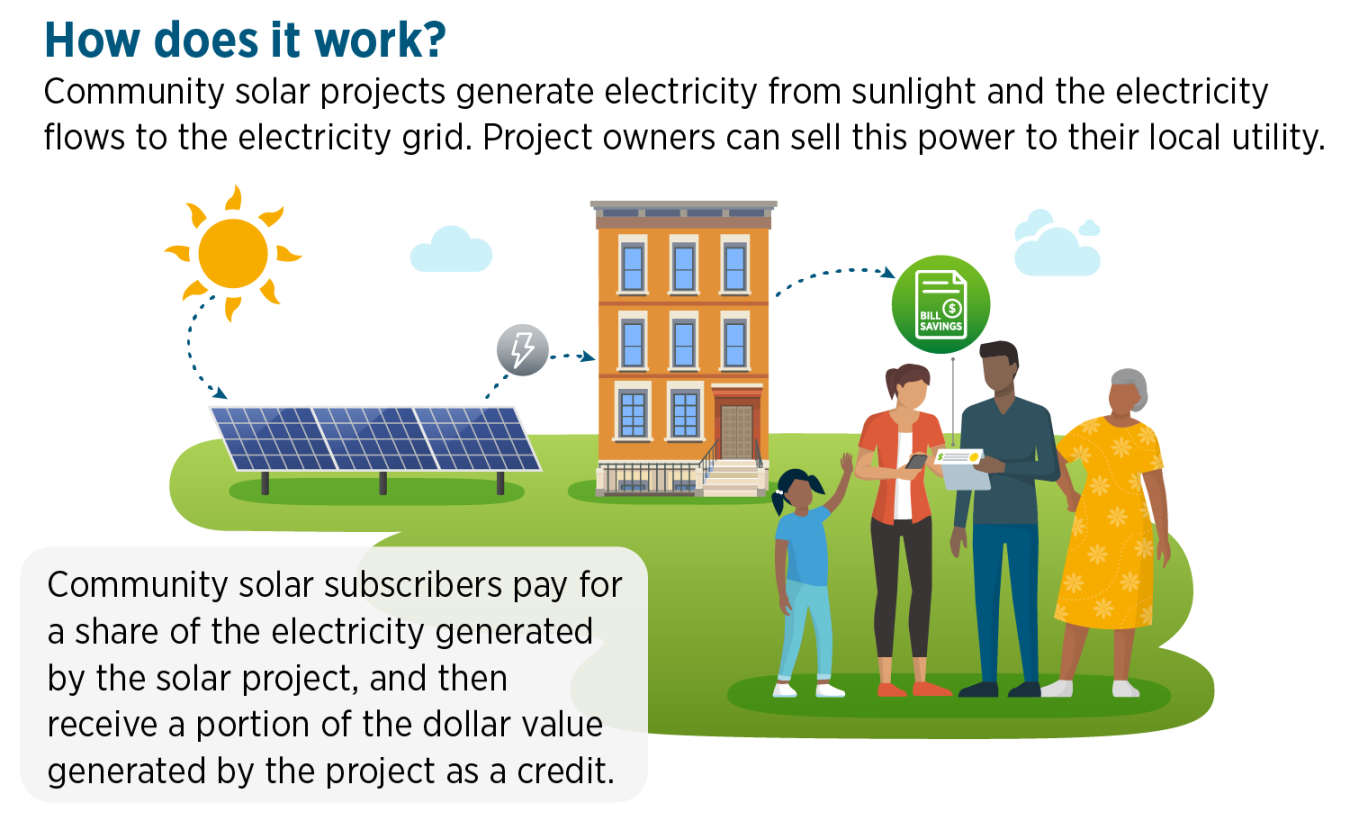
What Are Community Solar Projects?
Community solar projects are large-scale solar energy installations that are shared by multiple users. These projects allow individuals and businesses to invest in a solar array without the need for personal rooftop space or the upfront costs typically associated with residential solar installations. Instead, participants in community solar projects receive credits on their electricity bills for the energy produced by the solar farm, reducing their overall energy costs.
The concept is built on the idea of shared solar ownership, where a group of participants—residents, businesses, schools, or government buildings—can collectively benefit from solar energy. These projects can vary in size, from small installations serving a single neighborhood to large-scale facilities that power thousands of homes.
Types of Community Solar Programs
Community solar projects can be structured in various ways to meet the needs of different participants. Some of the most common types include:
- Subscription-based Community Solar: In this model, participants subscribe to a portion of the energy produced by the solar farm. They typically receive a monthly credit on their energy bill for the amount of energy produced by their share of the system.
-
Ownership-based Community Solar: This type of program allows participants to invest directly in the solar farm, owning a specific share of the system. The return on investment comes from energy credits earned from the solar farm’s output.
-
Virtual Net Metering (VNM): In VNM programs, solar energy is produced at a central location and then credited to individual participants’ utility bills, even if they are located far from the solar array. This allows for flexibility in terms of participant location and eliminates the need for each participant to be directly connected to the solar farm.
How Do Community Solar Projects Work?
The mechanics of a community solar project are relatively simple. Here’s how it works:
- Development: A developer or utility company builds a large solar installation, typically in an area with ample sunlight, such as rooftops, vacant land, or open fields.
-
Subscription or Investment: Individuals or businesses interested in accessing solar energy sign up for the project. This can involve subscribing to a share of the energy produced, or in some cases, making an investment to own part of the installation.
-
Energy Production: The solar array generates electricity from the sun’s energy, and the power is fed into the local grid.
-
Energy Credits: As the solar farm generates energy, the electricity is allocated to participants in the form of credits, which are applied to their utility bills based on the amount of energy they have subscribed to or invested in.
-
Savings on Utility Bills: Participants benefit by receiving energy credits, which lower their overall electricity costs. This allows them to enjoy the benefits of solar energy without the need for personal solar panels.

Benefits of Community Solar Projects
Community solar projects offer a range of benefits, both for individuals and society as a whole. Let’s look at some of the most significant advantages:
1. Lower Energy Costs
One of the main reasons people participate in community solar projects is the potential for lower energy bills. By subscribing to or owning a portion of a solar farm, participants can receive credits on their utility bills, often resulting in substantial savings. This is particularly helpful for those who may not be able to afford the upfront costs of installing solar panels on their own property.
2. Increased Access to Renewable Energy
Not everyone has the option to install solar panels on their roof, due to factors such as shading, roof orientation, or homeownership status. Community solar projects provide an opportunity for renters, homeowners with unsuitable roofs, and low-income households to access the benefits of solar power. This democratizes clean energy and expands access to renewable energy across various demographics.
3. Environmental Impact
By participating in community solar projects, individuals and businesses help to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, thereby decreasing their carbon footprint. Solar energy is one of the cleanest sources of power, and increased adoption of solar energy helps combat climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainability.
4. Community Engagement and Local Economic Development
Community solar projects foster local engagement and economic growth. By creating local solar farms, these projects generate jobs in construction, maintenance, and operation. Moreover, they often contribute to the local economy by supporting green technology and clean energy businesses.
5. Flexibility and Scalability
Community solar projects offer flexibility in terms of size and scale. These systems can be designed to meet the needs of a single neighborhood or a larger community. This scalability ensures that solar energy can be deployed in various regions, including urban, suburban, and rural areas, increasing its overall impact.
Challenges of Community Solar Projects
While community solar projects are promising, there are several challenges that need to be addressed to maximize their potential:
1. Regulatory Barriers
In many regions, regulatory frameworks may not be conducive to the development of community solar projects. In some cases, laws and policies may restrict the ability of individuals or businesses to participate in shared solar programs. Legislative changes are often needed to enable the widespread adoption of community solar.
2. Financing and Costs
Although community solar can help reduce energy costs, the initial investment required to develop and implement these projects can be significant. Securing financing and finding cost-effective models for all participants—especially low-income households—remains a challenge for developers.
3. Grid Access and Infrastructure
Community solar projects require access to the electric grid, and in some cases, the existing grid infrastructure may not be sufficient to handle the increased capacity. Upgrading the grid to accommodate community solar farms is an essential step in expanding their reach.
4. Availability and Local Demand
The availability of community solar projects depends on local demand and suitable sites for solar farms. In some regions, the potential for solar power is limited due to geographic conditions, and creating enough demand for a large-scale solar farm may prove challenging.
The Future of Community Solar Projects
Despite these challenges, the future of community solar is incredibly promising. Several trends and advancements indicate that community solar projects will become a more integral part of the global clean energy landscape:
- Expansion of Solar Programs: As awareness of community solar grows, more utilities, developers, and governments are supporting the creation of new community solar programs. This will increase access to solar energy and make it more affordable for a wider range of people.
-
Technological Advancements: Advances in solar panel efficiency and energy storage technologies are expected to make community solar projects more effective, reliable, and cost-efficient. This will improve the overall economics of solar energy for participants.
-
Collaboration between Stakeholders: Partnerships between governments, utilities, and private developers will be essential in overcoming regulatory barriers and securing financing for large-scale community solar initiatives.
-
Greater Equity and Inclusivity: Future community solar programs will likely focus on ensuring that low-income households, renters, and marginalized communities have equal access to the benefits of solar energy. These programs will prioritize inclusivity and energy justice.
FAQs About Community Solar Projects
1. How do I participate in a community solar project?
To participate, you can research local community solar programs, find one that fits your needs, and either subscribe to a share of the solar farm or invest in it. Many projects allow you to sign up directly through their websites or through a local utility provider.
2. Do I need to own a home to participate in a community solar project?
No, you do not need to own a home. Renters and homeowners with unsuitable roofs can participate in community solar programs, making them accessible to a broader range of people.
3. What happens if I move to a new location?
If you move to a new location within the service area of the community solar project, you can typically transfer your subscription to the new address. However, it’s important to check with the program administrator to understand specific terms.
4. Are community solar projects available in all areas?
Community solar programs are not yet available in all regions. Availability depends on local regulations and the willingness of utilities and developers to invest in these projects. However, as demand for clean energy grows, more projects are expected to launch in various regions.
Conclusion
Community solar projects are a game-changer in the pursuit of renewable energy. By allowing people to access solar power without the need for personal solar panels, these projects democratize energy access, reduce costs, and help fight climate change. As technology improves and barriers to adoption are overcome, community solar has the potential to transform how we generate and use energy—creating a more sustainable, equitable, and resilient energy future.


