Blockchain in Supply Chain: Revolutionizing the Future of Global Trade
The blockchain technology has become a significant disruptor across multiple industries, and its potential to revolutionize supply chain management is no exception. This decentralized, secure, and transparent digital ledger has the power to transform the way businesses track, verify, and manage the flow of goods and services across global networks.
In this article, we will explore how blockchain technology is changing the face of supply chains, enhancing efficiency, transparency, and security while addressing some of the industry’s most pressing challenges.
What is Blockchain and How Does It Work?
At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that securely records transactions across multiple computers in a way that ensures the data cannot be altered or tampered with. Each “block” of data is connected to the previous one, forming a chain, which is why it is called a blockchain.
This immutable nature of the blockchain makes it ideal for applications where transparency, trust, and security are critical — like in supply chain management.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology:
- Decentralization: No central authority controls the blockchain, meaning it operates on a peer-to-peer network.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to authorized parties, ensuring accountability.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded, it cannot be changed or deleted, ensuring integrity.
- Security: Blockchain uses cryptographic algorithms to secure data, making it resistant to hacking.

How Blockchain is Transforming Supply Chain Management
The traditional supply chain model faces various challenges, such as lack of visibility, fraud, inefficiency, and miscommunication. Blockchain’s decentralized and transparent nature solves these problems by providing real-time, tamper-proof data that all stakeholders can trust.
Here are some ways blockchain is revolutionizing supply chains:
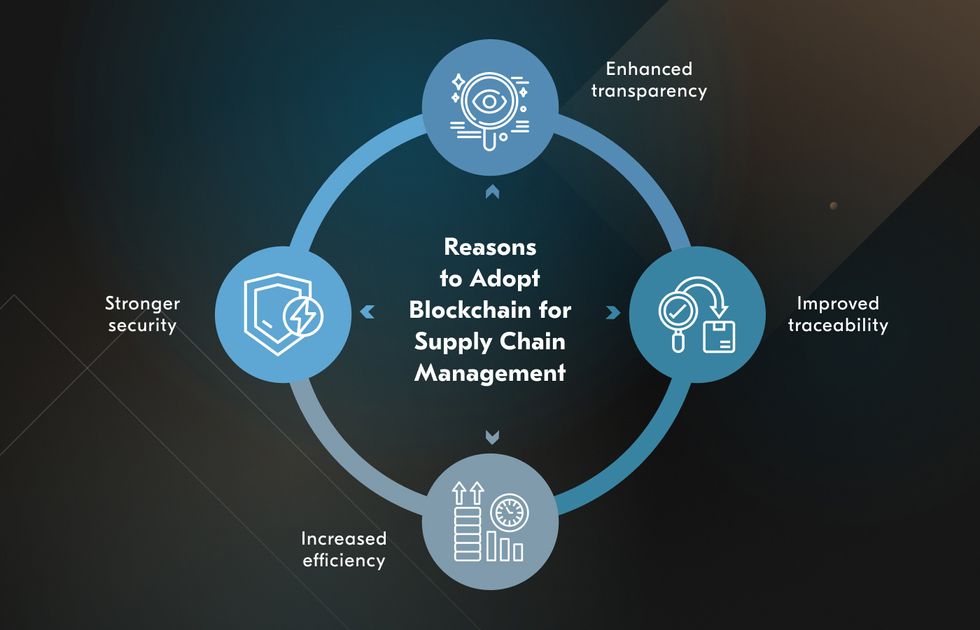
1. Enhanced Transparency and Traceability
One of the most significant benefits of blockchain in supply chains is improved transparency. By creating a shared, immutable ledger, blockchain allows each participant in the supply chain — from raw material suppliers to end customers — to track the product’s journey.
For example, imagine tracking the origins of a product, such as a luxury item or food product. With blockchain, every step of its production, from sourcing to final delivery, is recorded. This increases consumer confidence and ensures that suppliers adhere to ethical and regulatory standards.
Example Use Case:
Walmart and IBM have partnered to use blockchain to track the origin of food products, which helps ensure food safety and reduces contamination risks.
2. Increased Efficiency and Reduced Costs
Traditional supply chains rely on paper-based processes and intermediaries, which can be slow, costly, and prone to error. Blockchain automates many of these manual tasks through smart contracts — self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code.
By automating processes such as payment settlements, order fulfillment, and inventory management, blockchain streamlines operations and reduces the costs associated with intermediaries and administrative overhead.
Example Use Case:
De Beers, a leader in the diamond industry, has implemented blockchain to track diamonds through the entire supply chain. This not only ensures authenticity but also improves efficiency and cuts out unnecessary intermediaries.
3. Improved Security and Fraud Prevention
The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that no single party can manipulate or alter the transaction data. This makes blockchain an incredibly secure technology that helps prevent fraud, counterfeiting, and theft.
In sectors like pharmaceuticals and luxury goods, blockchain helps ensure that the products are genuine and not counterfeited or tampered with. The ability to securely track items from their origin to the consumer ensures that every product is as claimed.
Example Use Case:
Maersk, the world’s largest container shipping company, uses blockchain to improve the security and efficiency of its shipping documentation, ensuring cargo is handled securely throughout its journey.
4. Faster Payments and Settlements
Blockchain enables faster and more efficient payment processes. Using cryptocurrency or blockchain-based tokens, supply chain partners can settle payments instantly without the need for banks or third-party intermediaries.
By speeding up payments, businesses can improve their cash flow and reduce the financial strain on suppliers, which is especially important in industries with tight margins or long payment cycles.
Example Use Case:
The trade finance company, Contour, uses blockchain to automate and streamline the settlement of international trade payments, reducing processing times from days to hours.
5. Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Blockchain can play a key role in ensuring that supply chains are sustainable and adhere to ethical standards. By providing transparency into each step of a product’s lifecycle, companies can monitor their environmental impact and ensure they are not exploiting workers or engaging in unethical practices.
For instance, companies can use blockchain to trace the source of raw materials, ensuring they are responsibly sourced and do not contribute to deforestation or child labor.
Example Use Case:
The luxury goods brand Patagonia uses blockchain to trace the source of materials and ensure that their supply chain adheres to sustainability practices, helping the company reduce its environmental footprint.
6. Real-Time Data Sharing and Collaboration
Blockchain enables real-time, secure sharing of data among supply chain partners. This real-time data sharing leads to better collaboration and more informed decision-making.
For example, businesses can share inventory levels, demand forecasts, and shipment tracking data, helping reduce delays and improve responsiveness to changing market conditions.
Example Use Case:
Provenance, a blockchain-based platform, helps companies in the fashion and food industries share real-time information about the products’ journey, enhancing supply chain collaboration.
Challenges of Implementing Blockchain in Supply Chains
While blockchain offers numerous advantages, it is not without its challenges. Businesses looking to adopt blockchain for supply chain management should be aware of the following hurdles:
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating blockchain with legacy systems can be complex and costly.
- Scalability Issues: As the blockchain grows, the system may struggle with scalability, especially in industries with high transaction volumes.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Blockchain is still a relatively new technology, and regulations surrounding its use are still evolving.
How to Overcome These Challenges?
Businesses can overcome these challenges by:
– Working with blockchain experts to ensure proper integration with existing systems.
– Using scalable blockchain platforms that can grow with the business.
– Keeping abreast of evolving regulations and working with legal advisors to ensure compliance.

FAQs about Blockchain in Supply Chain
1. What are the key benefits of blockchain in supply chain management?
The key benefits include improved transparency, reduced costs, increased security, faster payments, and the ability to ensure sustainability and ethical practices.
2. Can blockchain prevent fraud in the supply chain?
Yes, blockchain’s immutable nature makes it highly effective in preventing fraud and counterfeiting by providing a transparent and secure way to track the journey of products from origin to end consumer.
3. How can blockchain improve supply chain efficiency?
Blockchain improves efficiency by automating tasks through smart contracts, reducing the need for intermediaries, and providing real-time data for better decision-making.
4. Which industries can benefit from blockchain in supply chains?
Industries such as food and beverage, luxury goods, pharmaceuticals, automotive, and textiles are already leveraging blockchain for supply chain improvements.
5. What is a smart contract in the context of blockchain?
A smart contract is a self-executing contract with the terms and conditions directly written into the code. It automatically enforces and executes the contract’s terms when the conditions are met.
The Future of Blockchain in Supply Chain
As businesses continue to recognize the transformative potential of blockchain, its application in supply chain management is expected to grow exponentially. With the ongoing development of more efficient, scalable blockchain platforms, the supply chain of the future will be faster, more secure, and more transparent.
To stay ahead in a competitive marketplace, companies must explore the possibilities of blockchain technology and adopt it to unlock the full potential of their supply chain operations.
Conclusion
Blockchain is poised to revolutionize the supply chain industry by providing greater transparency, security, and efficiency. From improving traceability to reducing costs and enhancing sustainability, the benefits of blockchain are undeniable.
Businesses looking to remain competitive must consider implementing blockchain in their supply chains to reap the long-term rewards. By doing so, they will not only improve their operations but also gain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving global marketplace.
For more information on how to implement blockchain in your supply chain, visit Turing and Acropolium for expert insights and success stories.

