Biomass Energy: A Sustainable Resource
In the modern world, where energy demands are on the rise, the need for renewable energy sources has never been greater. One such solution that is gaining widespread attention is biomass energy. Biomass is organic material that can be used to produce electricity, heat, and biofuels. It’s derived from plant and animal materials, making it a sustainable and carbon-neutral resource. This article will explore what biomass energy is, how it works, its benefits, and its role in building a sustainable future.

What is Biomass Energy?
Biomass energy is energy produced from organic materials, such as plants, wood, and agricultural or animal waste. These materials contain stored energy from the sun, which is released when burned or processed in other ways to produce usable energy.
Unlike fossil fuels, biomass energy is considered renewable because its sources can be replenished naturally over time. By using biological waste and residues, we can generate energy while minimizing environmental impact.
There are several forms of biomass energy, each with different methods of generation:
- Wood and Wood Waste: Includes logs, chips, and sawdust that are burned for heat or converted into biofuels.
- Agricultural Residues: Crop waste, such as corn stalks, rice husks, and wheat straw, can be converted into biofuels.
- Animal Waste: Manure and other organic matter can be processed to produce biogas or converted into electricity.
- Algae: Algae can be used to produce biofuels, offering a potential energy solution that doesn’t require large amounts of land or freshwater.
These materials are used in various processes, from direct combustion to advanced conversion technologies like gasification and fermentation, to generate energy.

How Biomass Energy Works
Biomass energy can be harnessed in several different ways, and the process typically depends on the material being used and the intended application. The most common methods of converting biomass to usable energy include:
1. Combustion
The most straightforward method is combustion, where biomass is burned to produce heat. This heat can be used directly for space heating or to produce steam, which drives a turbine connected to a generator, creating electricity.
2. Gasification
Gasification is a process that involves heating biomass in a low-oxygen environment to produce syngas (a mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane). This syngas can then be burned for power generation or converted into biofuels.
3. Fermentation
In fermentation, sugars in plant-based materials like corn or sugarcane are converted into ethanol (a type of biofuel). This is commonly used for transportation fuels.
4. Anaerobic Digestion
This method involves breaking down organic materials, such as food waste and manure, in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas (methane). The biogas can then be used for electricity generation, heating, or as a vehicle fuel.
5. Biofuels (Liquid Fuels)
Biofuels like biodiesel and ethanol are produced by converting plant materials like corn, soybeans, or algae into liquid fuels. These fuels can be used in internal combustion engines, reducing the need for petroleum.
Benefits of Biomass Energy
Biomass energy has many advantages that make it an appealing renewable energy source. Below are some of the key benefits:
1. Renewable Resource
Unlike fossil fuels, which take millions of years to form, biomass energy comes from organic matter that can be replenished on a relatively short timescale. This makes it a sustainable and renewable energy source, provided that the biomass is harvested responsibly.
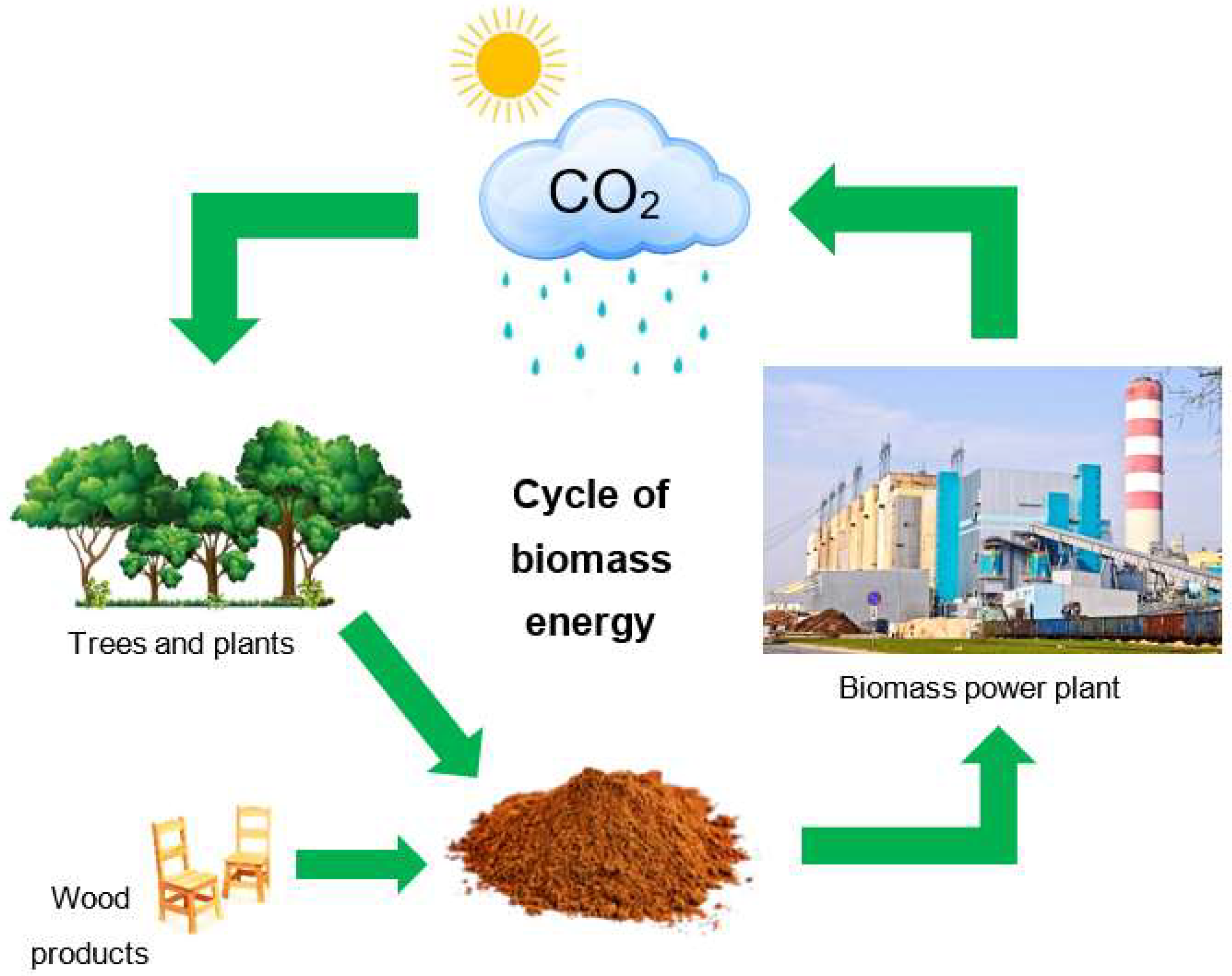
2. Carbon Neutral
When biomass is burned, it releases carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. However, the amount of CO2 released is roughly equivalent to the amount that was absorbed by the plants during their growth. This makes biomass energy carbon neutral, meaning it doesn’t contribute to net increases in greenhouse gases.
3. Waste Reduction
Biomass energy can help reduce the amount of organic waste that ends up in landfills. By converting agricultural, industrial, and municipal waste into energy, biomass can reduce waste and create useful byproducts, such as compost and biochar.
4. Economic Growth and Job Creation
The biomass industry creates jobs in agriculture, forestry, manufacturing, and energy production. It also helps stimulate local economies by providing a market for agricultural residues and other organic waste.
5. Energy Security
Biomass energy can contribute to energy independence by diversifying the energy mix. It allows regions to rely less on imported fossil fuels and instead use locally sourced organic materials for energy generation.
6. Grid Stability and Flexibility
Biomass energy plants can operate continuously, providing baseload power—a reliable source of energy that can be adjusted depending on demand. This makes biomass an important component of a balanced energy grid.
Applications of Biomass Energy
Biomass energy has a wide range of applications, from power generation to heating and biofuels. Some common uses include:
1. Electricity Generation
Biomass power plants convert biomass into electricity, much like traditional coal or natural gas plants. These plants can use direct combustion, gasification, or biogas to generate power.
2. Residential and Commercial Heating
Biomass heating systems can use wood, pellets, or other organic materials to heat buildings. These systems are becoming increasingly popular as an alternative to traditional heating methods like oil or natural gas.
3. Biofuels for Transportation
Biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel are commonly used in cars, trucks, and buses. These biofuels can be produced from a variety of sources, including corn, soybeans, and algae.
4. Industrial Use
Biomass is also used in industrial processes, such as cement production and paper manufacturing. In these applications, biomass can replace coal and other non-renewable fuels, reducing the environmental impact of manufacturing processes.
Biomass and Its Role in the Future
As the world transitions to more sustainable energy sources, biomass is expected to play a significant role. With its ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, provide renewable energy, and help manage organic waste, biomass offers an important solution for a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Countries like the United States, Brazil, and Sweden are already leading the way in biomass energy production, and there is growing interest in expanding biomass’s role in the global energy mix. By investing in research and technology, biomass energy could become an even more effective solution for meeting the world’s energy needs while reducing environmental harm.
FAQs About Biomass Energy
1. What is the most common source of biomass energy?
The most common sources of biomass energy are wood, agricultural residues, and animal waste. These materials can be used for combustion, biofuel production, or biogas generation.
2. Is biomass energy sustainable?
Yes, biomass energy is sustainable as long as the organic materials used are replenished at a rate that does not exceed their growth. Proper land management practices are key to maintaining biomass as a renewable resource.
3. How efficient is biomass energy?
Biomass energy is relatively efficient, with conversion technologies such as combustion and gasification achieving efficiency rates of 25-35%. However, new technologies and improved systems are continually increasing its efficiency.
4. Can biomass energy reduce carbon emissions?
Biomass energy can reduce carbon emissions compared to fossil fuels because it is considered carbon neutral. While it releases CO2 during conversion, the amount released is offset by the CO2 absorbed during plant growth.
Conclusion
Biomass energy is a renewable and sustainable solution that plays a vital role in the global transition to cleaner energy. With its ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, create jobs, and manage waste, biomass is an energy resource that has the potential to power the future. As technology advances and sustainability practices improve, biomass energy will continue to evolve and become an increasingly important part of our energy landscape.