Periodontal (Gum) Disease Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
Periodontal disease, often referred to as gum disease, is a common yet serious condition that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting your teeth. If left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss and other severe health complications. Fortunately, periodontal disease treatment is available and can help restore your gum health, preventing further damage.
In this article, we will dive deep into what periodontal disease is, its stages, treatment options, and preventive measures to help you maintain healthy gums for a lifetime.
What is Periodontal Disease?
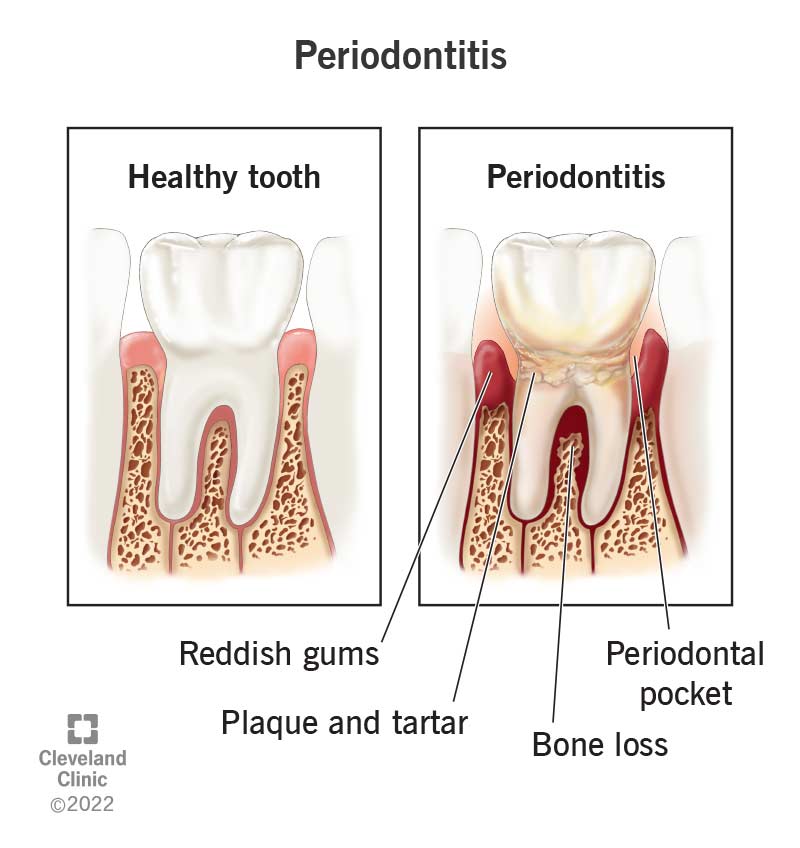
Periodontal disease is an infection of the tissues that support the teeth, including the gums, periodontal ligament, and bone. The condition typically develops from poor oral hygiene practices that allow plaque—a sticky, colorless film of bacteria—to build up on teeth and harden.
If plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it turns into tartar (calculus), which can only be removed by a dentist or hygienist. As tartar builds up, it irritates the gums, leading to inflammation. This early stage of gum disease is called gingivitis, which, if untreated, can progress to periodontitis.
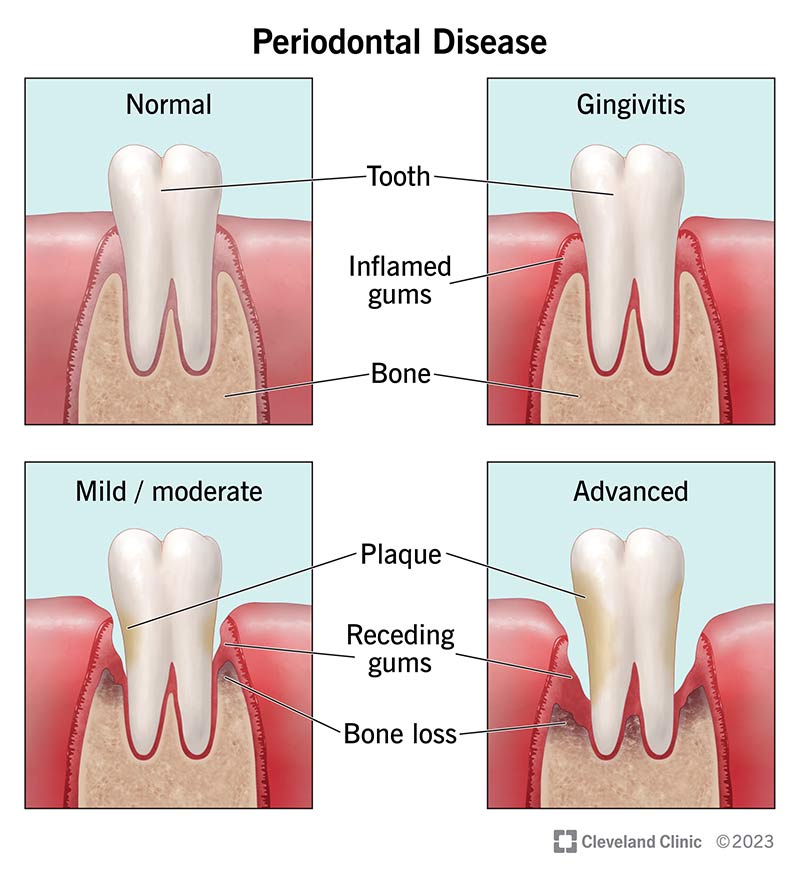
Stages of Periodontal Disease
- Gingivitis:
- This is the earliest stage of gum disease, characterized by red, swollen gums that may bleed when brushing or flossing. Gingivitis is usually reversible with proper dental care.
- Periodontitis:
- In this stage, the infection spreads deeper into the tissues, causing damage to the bone and tissues that support the teeth. You may notice pockets forming between the teeth and gums, leading to loosening of teeth.
- Advanced Periodontitis:
- In advanced stages, teeth can become so loose that they may need to be extracted. Bone loss and gum recession can severely impact your ability to chew and speak comfortably.
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease often develops silently, and many people may not notice symptoms until the condition is more advanced. Common signs of gum disease include:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially while brushing or flossing
- Bad breath or a persistent bad taste in the mouth
- Loose teeth or teeth that are shifting
- Gum recession, or gums that pull away from the teeth
- Pus between the teeth and gums
If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to seek professional treatment immediately to prevent the disease from progressing.
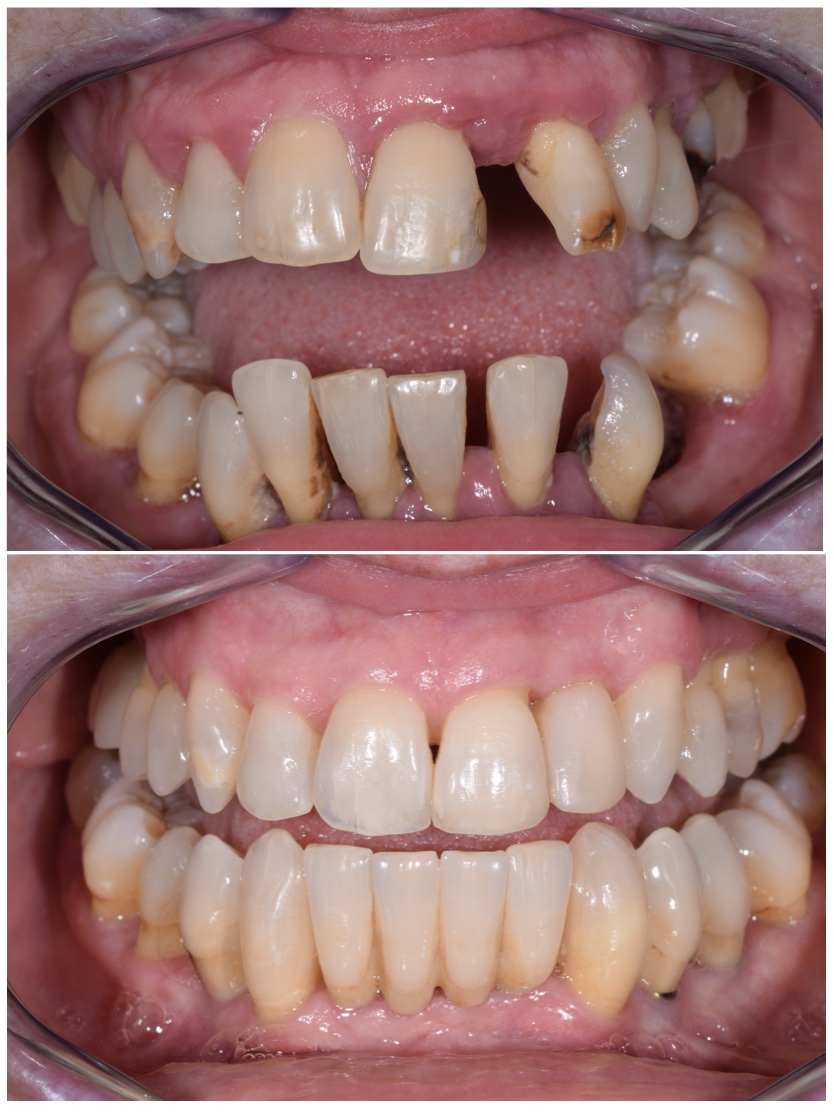
Treatment Options for Periodontal Disease
The goal of periodontal disease treatment is to control the infection, stop the progression of the disease, and restore the health of the gums and supporting structures. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the condition.
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
In the early stages of gum disease, non-surgical treatments can help reverse the damage. These treatments are typically used for gingivitis and mild periodontitis.
- Scaling and Root Planing:
- This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from the surface of the teeth and below the gumline. Scaling is performed to remove plaque, while root planing smooths the tooth roots to help the gums reattach to the teeth.
- Scaling and root planing is the most common non-surgical procedure used to treat periodontal disease.
- Antibiotics:
- Antibiotics, either in the form of oral medication or topical gels applied directly to the gums, can help control infection and reduce inflammation. These are often used in conjunction with scaling and root planing.
2. Surgical Treatments
For more advanced stages of periodontal disease, surgical treatments may be necessary to repair and regenerate the damaged tissues.
- Flap Surgery:
- Flap surgery involves making small incisions in the gums to lift them back and access deeper areas of infection. This procedure allows the dentist to remove tartar from the roots and smooth the bone surface.
- After the surgery, the gums are sutured back in place to promote better healing and reattachment to the teeth.
- Bone Grafts:
- In cases of significant bone loss, a bone graft may be performed to regenerate bone around the teeth. This procedure uses bone from your body, a donor, or synthetic material to encourage bone growth.
- Soft Tissue Grafts:
- If gum recession has caused significant damage, a soft tissue graft may be necessary to replace lost gum tissue. This procedure involves taking tissue from another part of the mouth (usually the roof of the mouth) and attaching it to the receded area.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration:
- This procedure involves placing a special membrane between the gum and bone to encourage the growth of new bone and tissue. It’s typically used when bone loss has occurred, and the aim is to regenerate lost tissue.
3. Laser Treatment
In some cases, lasers may be used to treat periodontal disease. Laser therapy can be employed for both soft and hard tissue, helping to remove diseased tissue and stimulate the healing of healthy tissues. This approach is minimally invasive and often results in less bleeding and a faster recovery.
Home Care and Preventive Measures
While professional treatment is essential, home care plays a crucial role in managing and preventing the recurrence of periodontal disease. Adopting a good oral hygiene routine can significantly reduce your risk of developing gum disease.
1. Brushing and Flossing
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle strokes to avoid injuring your gums.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and below the gumline, where your toothbrush may not reach.
2. Antimicrobial Mouthwash
- Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria in the mouth, thus preventing plaque buildup and gum infection.
3. Regular Dental Checkups
- Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and checkups. Your dentist can detect the early signs of periodontal disease before it progresses to more severe stages.
4. Lifestyle Changes
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease, as it weakens your immune system and makes it harder for your gums to heal.
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and vitamins, particularly Vitamin C, which supports gum health.
Complications of Untreated Periodontal Disease
If left untreated, periodontal disease can have serious consequences, including:
- Tooth loss: As the disease progresses, the bone supporting the teeth may deteriorate, leading to tooth mobility and eventual loss.
- Systemic health issues: Studies have shown a link between periodontal disease and various systemic conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory issues. The bacteria from gum disease can enter the bloodstream, affecting other parts of the body.
FAQs About Periodontal Disease Treatment
Q1: Can periodontal disease be reversed?
A1: In the early stages of gum disease (gingivitis), it is reversible with proper treatment. However, in more advanced stages (periodontitis), treatment can help control the disease and prevent further damage but cannot fully reverse the effects.
Q2: Is periodontal treatment painful?
A2: While some discomfort may occur during and after treatment, most people find that the pain is manageable with prescribed painkillers. Non-surgical treatments like scaling and root planing are usually well-tolerated.
Q3: How long does it take to recover from periodontal surgery?
A3: Recovery time varies depending on the procedure and individual factors, but most patients can expect to resume normal activities within 1-2 weeks after surgery.
Q4: Can periodontal disease affect my overall health?
A4: Yes, research has linked periodontal disease to various systemic conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Managing gum health is important for overall wellness.
Q5: How often should I see my dentist for periodontal maintenance?
A5: After periodontal treatment, you will likely need to visit your dentist every 3-4 months for maintenance cleanings to ensure the disease doesn’t return.
Conclusion
Periodontal disease is a serious condition that requires timely and effective treatment to prevent long-term complications. Whether through non-surgical procedures, surgical treatments, or preventive care, there are many options available to restore gum health and protect your teeth.
If you suspect you have gum disease or are experiencing any symptoms, consult your dentist immediately to discuss treatment options. With early intervention and proper care, you can maintain healthy gums and enjoy a lifetime of good oral health.
For more information on gum health and periodontal treatments, visit Cleveland Clinic.